
|
ur_ros_rtde_tutorials package from ur_ros_rtde reposimple_ur10e_description simple_ur10e_moveit_config ur_ros_rtde ur_ros_rtde_gripper_commands ur_ros_rtde_msgs ur_ros_rtde_simple_clients ur_ros_rtde_tutorials |
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 0.0.0 |
| License | BSD-3-Clause |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Description | ROS2 Interface for Universal Robots CoBots based on ur_rtde (Python, C++) |
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/superdiodo/ur_ros_rtde.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | main |
| Last Updated | 2025-03-27 |
| Dev Status | UNMAINTAINED |
| CI status | No Continuous Integration |
| Released | UNRELEASED |
| Tags | python cpp python3 ros universal-robots ros2 moveit2 rtde rviz2 ros2-humble |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (0)
Good First Issues (0) Pull Requests to Review (0) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- Alessio Saccuti
Authors
Tutorials for ur_ros_rtde
The proposed software is composed of three ROS2 nodes:
-
RobotStateReceiver ) provides robot data through topics and services (reference file:
ur_ros_rtde/launch/robot_state_receiver.launch.py). -
CommandServer ) discovers and loads
ur_ros_rtde_commandsandur_ros_rtde_extensionplugins available in the ROS2 workspace. Each plugin starts a ROS2 action server. Reference files: -
DashboardServer ) discovers and loads
ur_ros_rtde_dashboard_commandsplugins available in the ROS2 workspace. Each plugin starts a ROS2 action server. Reference files:
You can easily interact with ROS2 services and actions using header files provided in ur_ros_rtde_simple_clients. For further details and documentation, please visit ur_ros_rtde.
Run examples
Ensure that the ur_ros_rtde_tutorials package is compiled.
Retrieve robot state
To retrieve the robot state RobotStateReceiver must be used.
- Configure
robot_state_receiver.launch.py:- set ip address with
robot_ip
- set ip address with
- Launch robot_state_receiver:
# type in a new terminal
ros2 launch ur_ros_rtde robot_state_receiver.launch.py
At this point, the robot state can be accessed using topics and services.
- Print joint states:
# type in a new terminal
ros2 topic echo /joint_states
Visualize the robot in RViz
RobotStateReceiver does not require any URDF of the robot, but URDF files are required to visualize the robot in tools like RViz. If a ROS2 description package of a UR robot is already available, skip to step 2 and use that package instead of simple_ur10e_description.
- In
simple_ur10e_descriptiongenerate UR10e URDF file from xacro files.
# generate ur10e urdf
cd ~/your_path/simple_ur10e_description/urdf
sh generate_urdf.sh ur10e.xacro ur10e.urdf
# build again the package to make the urdf visible
cd <ros_workspace_path>
colcon build --symlink-install --cmake-args -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release --packages-up-to simple_ur10e_description
- Configure
robot_state_receiver.launch.py:- set ip address with
robot_ip - set
robot_description_package = "simple_ur10e_description" - set
urdf_file_name = "urdf/ur10e.urdf" - set
launch_rviz = True
- set ip address with
When setting launch_rviz to True a robot state publisher node is started which will publish TF for each robot link based on the joint states.
- Launch RobotStateReceiver:
# type in a new terminal
ros2 launch ur_ros_rtde robot_state_receiver.launch.py
The first time RViz will be empty. To show the robot:
1. Add a robot model: `Displays\Add\RobotModel`
2. Set `world` in `Fixed Frame`
3. Set `/robot_description` in `RobotModel\Description Topic`
4. Click on `File\Save config` to save the actual configuration of RViz
Activate robot commands
In ur_ros_rtde commands are defined as plugins and exposed as action servers. To make available these action servers the CommandServer must be started:
-
Configure
command_server.launch.pysetting ip address withrobot_ip -
Launch CommandServer:
# type in a new terminal
ros2 launch ur_ros_rtde command_server.launch.py
- List the available commands (more info at ur_ros_rtde):
# type in a new terminal
ros2 action list
The file command_server.launch.py can also be used to define a blacklist of plugins which must not be loaded. By default, the plugins implemented in ur_ros_rtde_gripper_commands are disabled, since they rely on the presence of specific hardware.
Move the robot
In this tutorial package are provided 3 examples which can be used to move the robot:
-
Execute linear movements: The robot performs small linear movements along the X-axis printing the robot pose after each movement. The robot state is retrieved with services exposed by RobotStateReceiver. Commands are sent to the robot with the CommandServer.
- Configure and launch RobotStateReceiver, set
launch_rviz = Trueif you want to see the robot moving in RViz:
- Configure and launch RobotStateReceiver, set
# type in a new terminal
ros2 launch ur_ros_rtde robot_state_receiver.launch.py
-
Configure
command_server.launch.pysetting ip address withrobot_ip. -
Launch CommandServer:
# type in a new terminal
ros2 launch ur_ros_rtde command_server.launch.py
-
Run executables:
WARNING! If everything was successfully configured the robot will start moving! Check for possible collisions with the environment!
With
linear_movementsexecutable MoveL commands are sent to the robot. Starting from the actual pose it will move +10 cm on X axis, then -20 cm on X axis and finally +10 on X axis again.
# type in a new terminal
ros2 run ur_ros_rtde_tutorials linear_movements
-
Execute a waypoint-based trajectory: In
trajectory_executionthere is an example in which a trajectory is sent to the robot. The robot (oriented towards Y-axis) will move as shown in the animated image.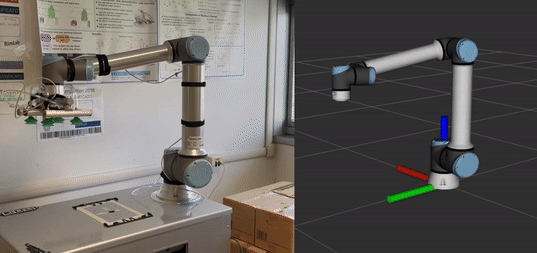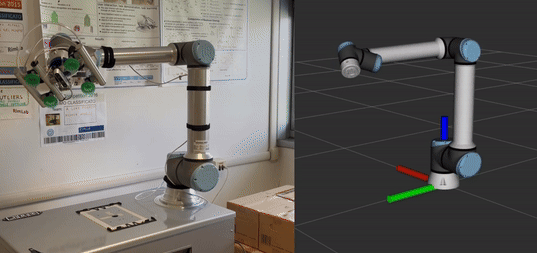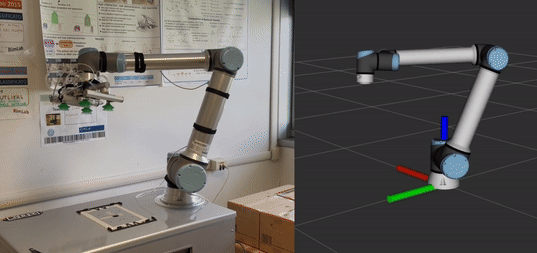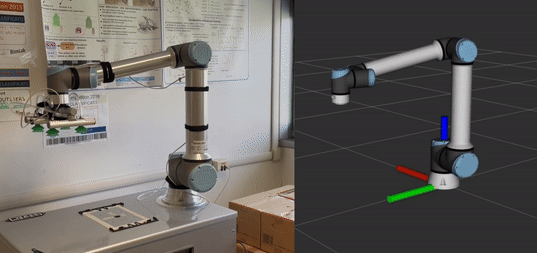
This example only requires an instance of the CommandServer and can be executed as shown below:
# type in a new terminal
ros2 run ur_ros_rtde_tutorials trajectory_execution
Adding new commands to ur_ros_rtde
In ur_ros_rtde/src/base_commands and ur_ros_rtde/src/base_dashboard_commands there is the implementation of several commands which are exposed as ROS2 plugins. When launching CommandServer and DashboardServer these plugins are automatically loaded.
In this package and ur_ros_rtde_gripper_commands and are provided examples of how new commands can be implemented as ROS2 plugins. For instance, in this package there is an example of implementation of the MoveDownUntilForce plugin, which allow to move the robot towards the ground until a force is detected.
If ur_ros_rtde_tutorials is compiled, the plugin will be loaded automatically by the CommandServer. The command can be sent to the robot sending an empty goal to the corresponding action server:
- Launch CommandServer:
# type in a new terminal
ros2 launch ur_ros_rtde command_server.launch.py
- Send the goal:
# type in a new terminal
ros2 action send_goal /ur_ros_rtde/move_down_until_force_command ur_ros_rtde_tutorials/action/MoveDownUntilForce {}

Integration of ur_ros_rtde and MoveIt!
Setting launch_moveit = True in ur_ros_rtde/launch/robot_state_receiver.launch.py, several files from the associated MoveIt! configuration package are automatically launched.
Wiki Tutorials
Package Dependencies
| Deps | Name |
|---|---|
| ur_ros_rtde | |
| ament_cmake_ros | |
| rosidl_default_generators | |
| rosidl_default_runtime | |
| ament_lint_auto | |
| ament_lint_common | |
| ur_ros_rtde_msgs |