
|
global_localizer package from kidnapped_robot_finder repoglobal_localizer |
Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 0.0.0 |
| License | TODO: License declaration |
| Build type | AMENT_PYTHON |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Description | This repository contains ROS2 package for 2d-Lidar scanner based Kidnapped Robot Re-localization solution (without using AMCL). The idea is to take the original map image, and create a scan-image from local lidar scan, then 'simulate' scans on random positions in the map image (using ray-casting), and find the best-matching scan with orig scan. |
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/saadi-tech/kidnapped_robot_finder.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | main |
| Last Updated | 2024-12-25 |
| Dev Status | UNMAINTAINED |
| CI status | No Continuous Integration |
| Released | UNRELEASED |
| Tags | opencv mapping lidar transformation ros2 slam-algorithms feature-matching kidnap-robot robot-recovery |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (0)
Good First Issues (0) Pull Requests to Review (0) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- saad
Authors
Global Localizer / Kidnap pose solver
This ROS2 package is dedicated to estimate the position of a ‘kidnapped’ mobile robot in a given map. This package will find estimate the robot’s current position in the map, by matching the features in the lidar-scan with the map’s features. The output of this package can be used to give initial pose estimate to other localizers like AMCL.
Assuming the robot is equipped with a 2d Lidar scanner, this package takes following inputs:
- Map image (.png).
- Current lidar scan (from a published topic: “/scan” by default)
Description
This package contains works on an innovative approach to estimate the position of a kidnapped robot in a 2d map. It uses following approach:
- Read map_image.
- Take lastest 2d lidar scan from the robot, create a scan_image (keeping lidar at the center)
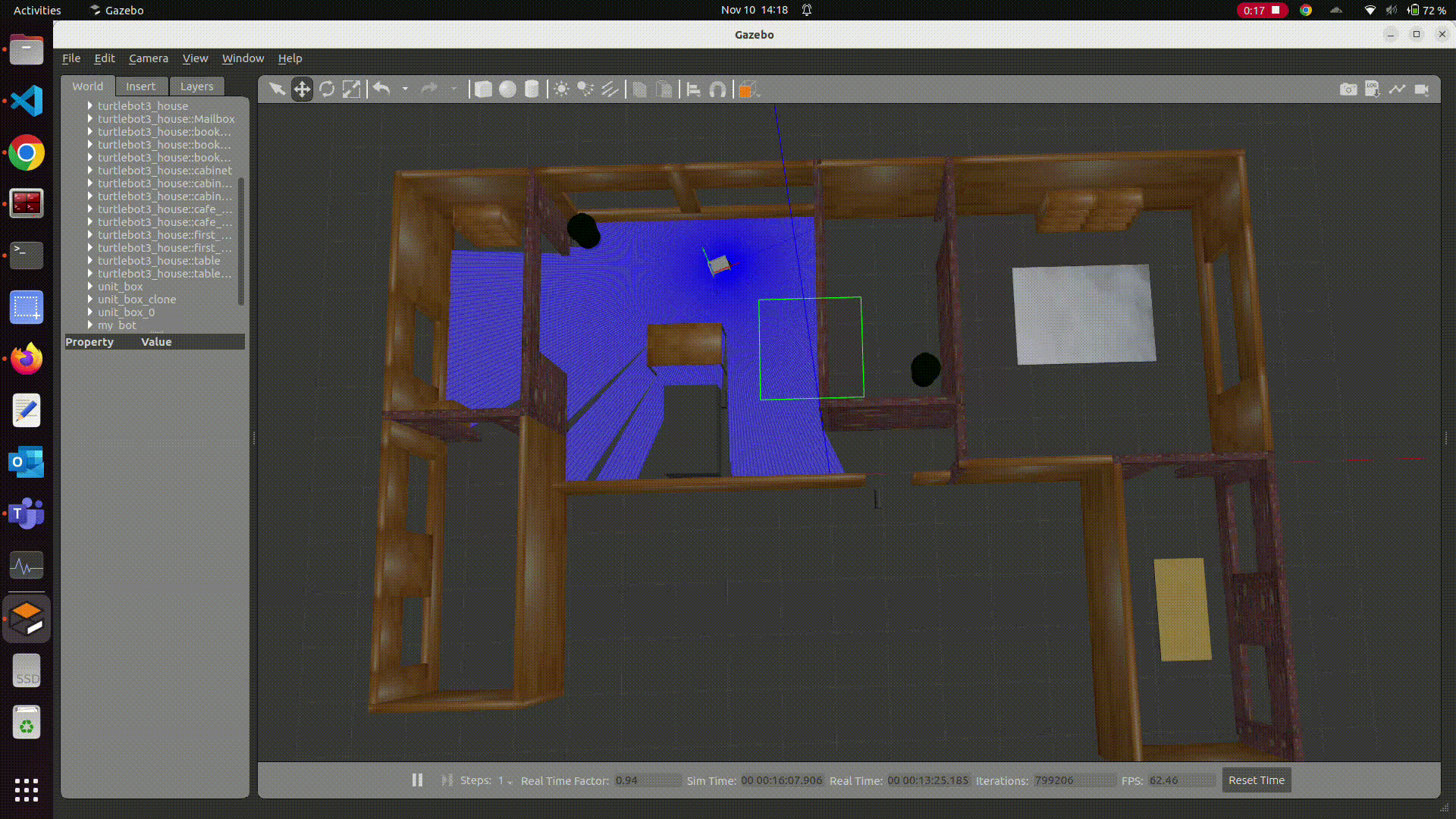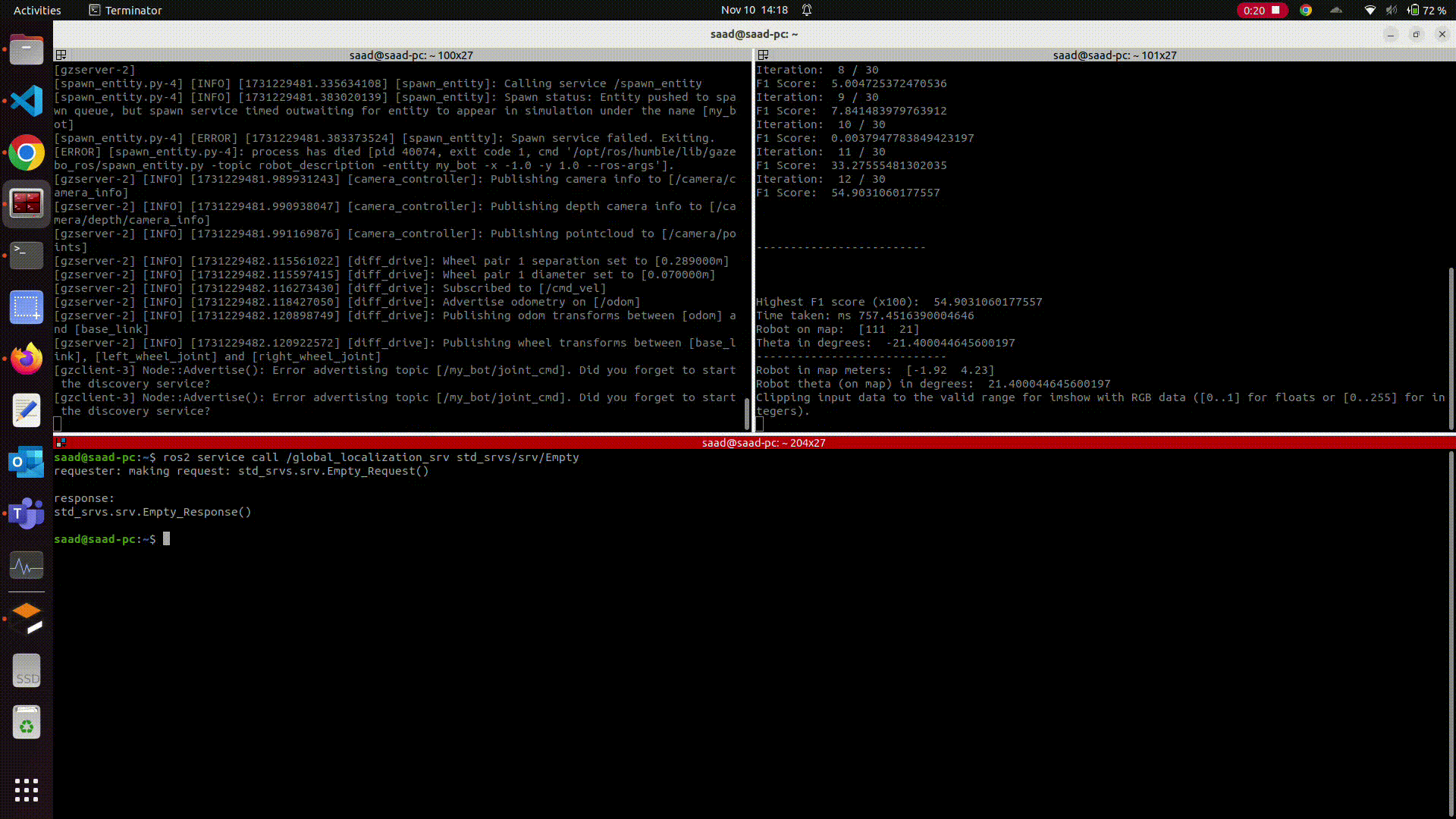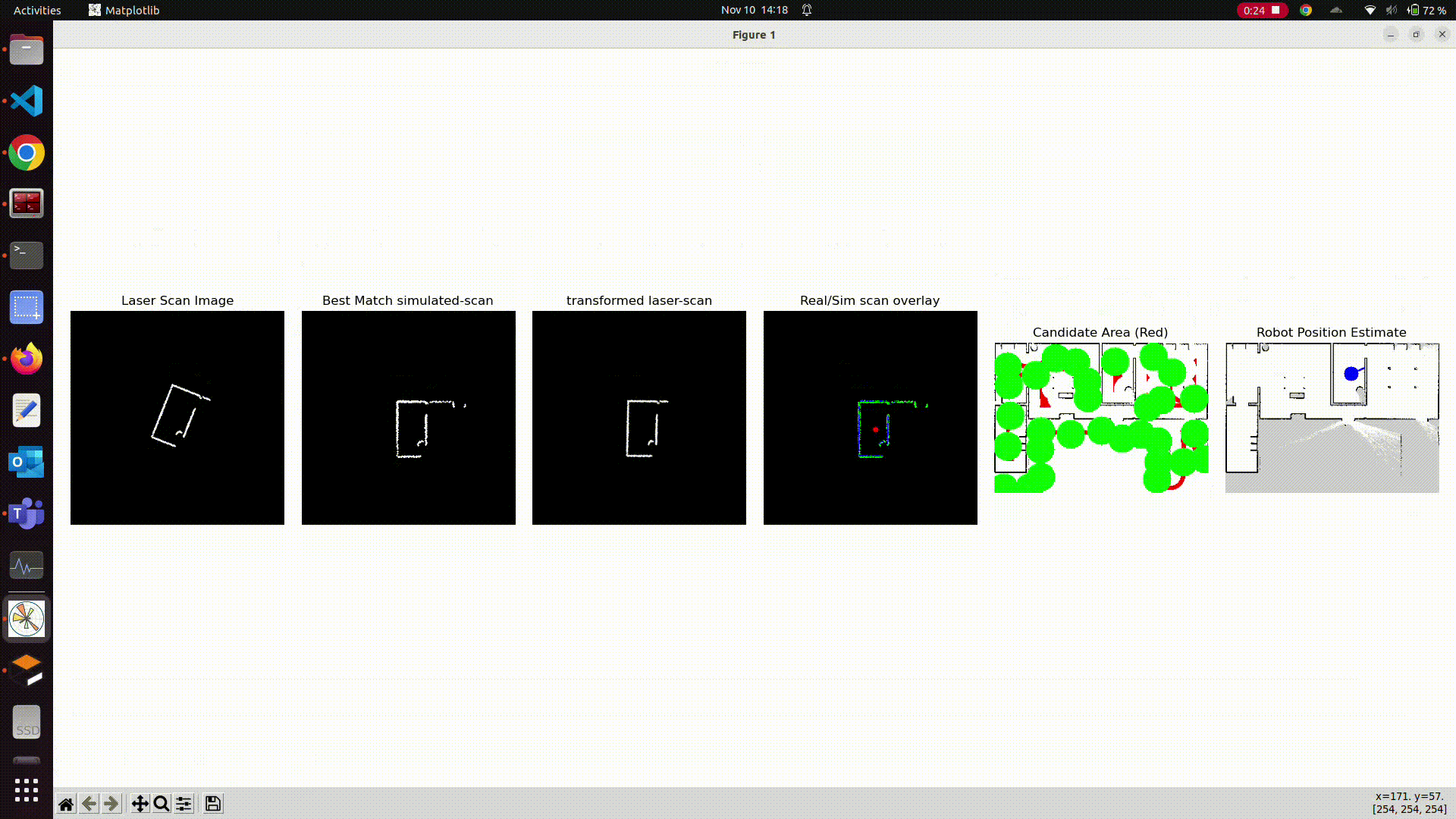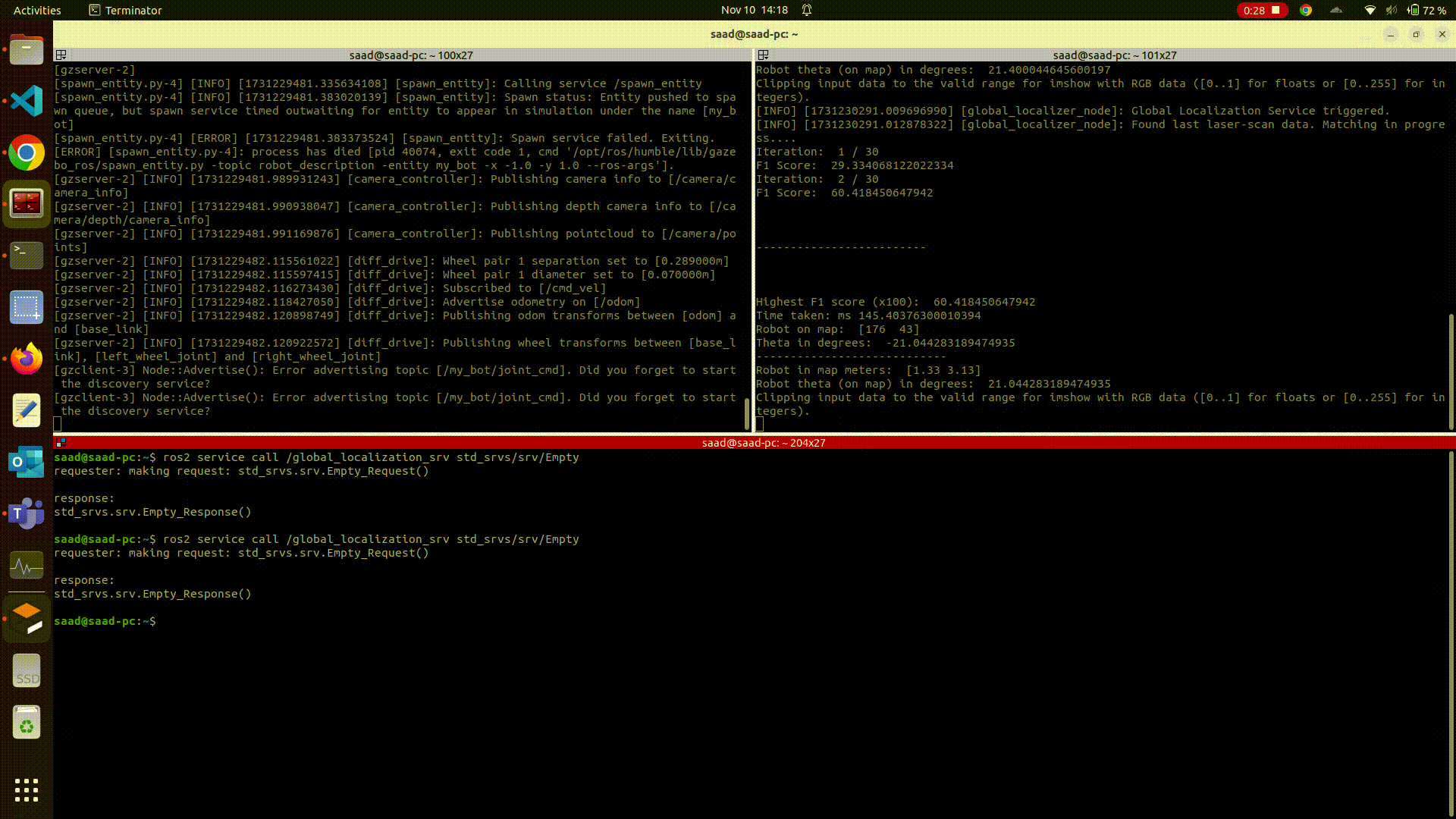
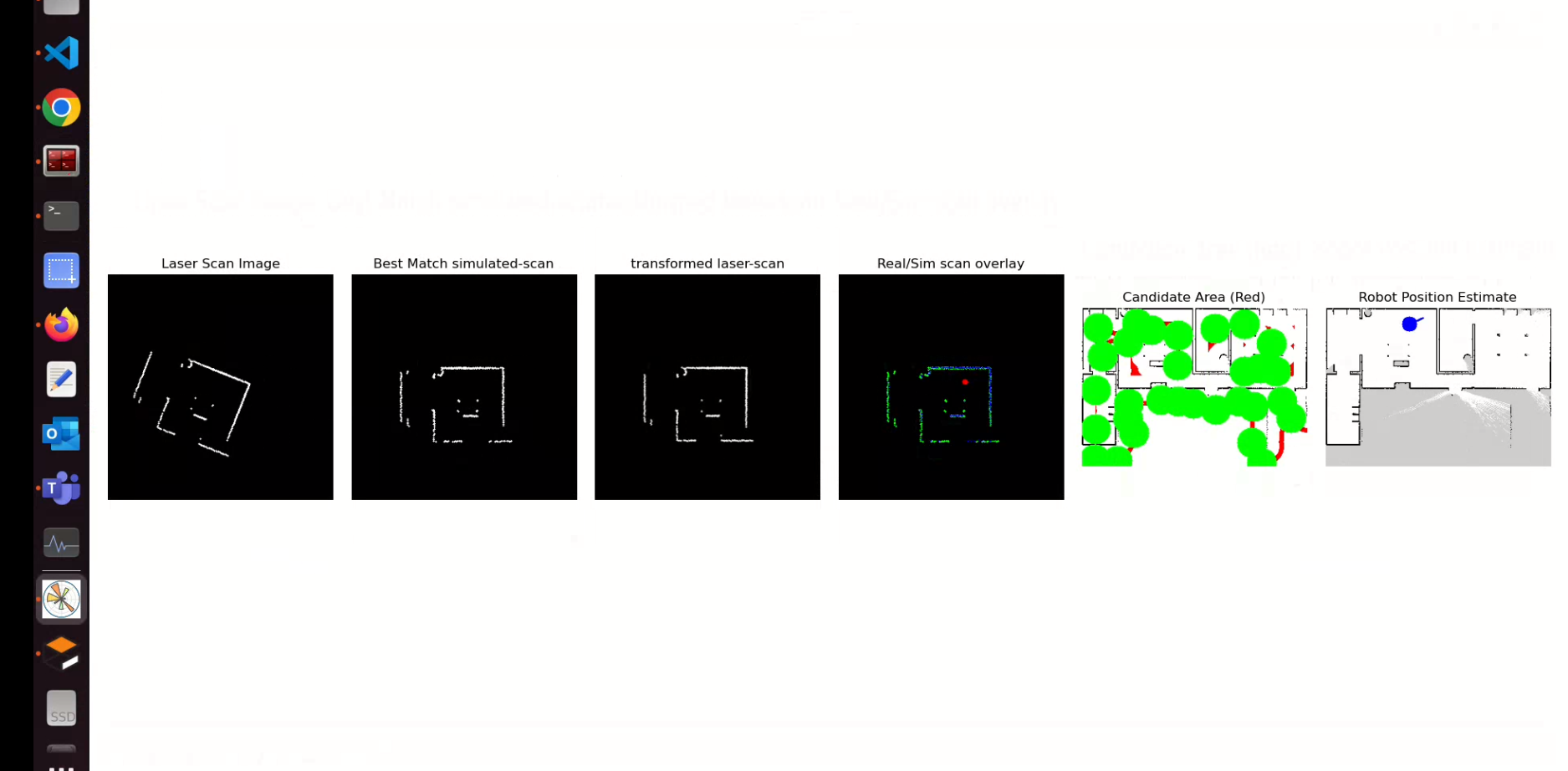
- ‘Simulate’ scans on the map: Use the map-image and lidar parameters to simulate scans on different positions on the map (using ray-casting), i.e. how the scan would look like if the robot is present at that specific position (by using map_image).
- Compare those simulated scans with original scan_image, find ORB features using openCV, match them and find the transform between simulated & original scan.
- Align the simulated and original scan with the previously found affine transformation.
- Find the best ‘aligning’ simulated scan with the original scan using F1 score metric.
- Use the best aligned simulated scan to then calculate the position of the robot on the map.
Currently, the output is Uni-modal (it will give the highest probable position of the robot). But I will further make it multi-modal (to give multiple position estimates if there are similar locations in the map.)
Instead of taking random points on the map (as candidate positions), this package uses an optimized approach. It gets the distance to the closest obstacle from the lidar scan, and selects ONLY the area on the map which has almost similar distance to nearest obstacle pixels. Then we select the candidates by adaptive randomized selection. It helps us to reduce the search area by a big factor, so we get very good results in very few iterations.
Installation
This package was developed and tested on ROS2 Humble:
- Clone the repository & build the workspace after adding the correct configurations in config.yaml file.
Usage
To use the Global Localizer package, follow these steps:
- Add the “absolute” path to map-image (in image formats e.g. png) in the config.yaml file, and rebuild the package.
- Launch the simulated/real robot, make sure the /scan topic is publishing the current scan.
- Initialize the localization service: ‘ros2 run global_localizer global_localizer’
- The service would be ready, you can call the kidnap solving solution by: ‘ros2 service call /global_localization_srv std_srvs/srv/Empty’
- It will run the iterations and find the best, probable position for the kidnapped robot.
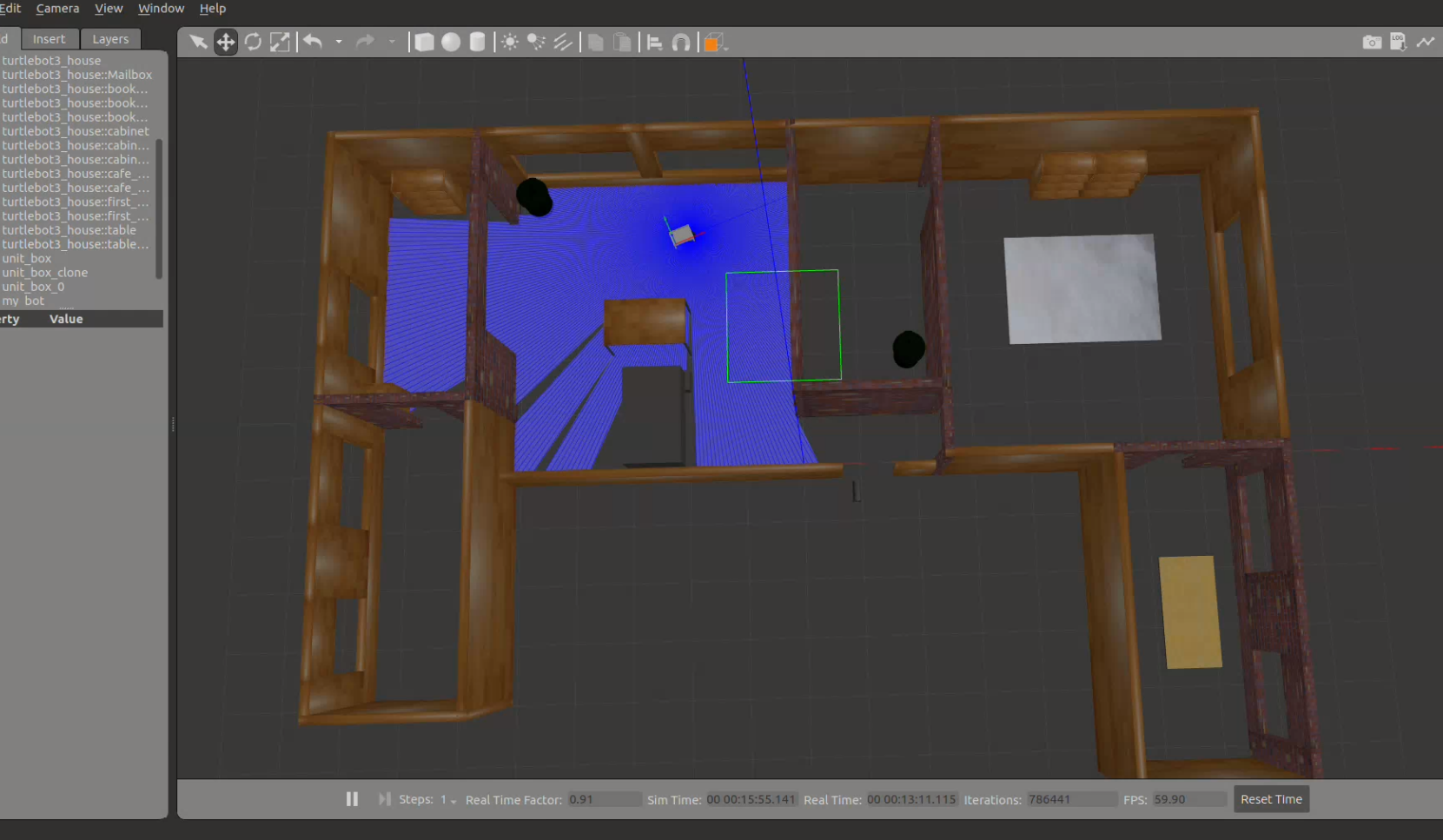
Demo
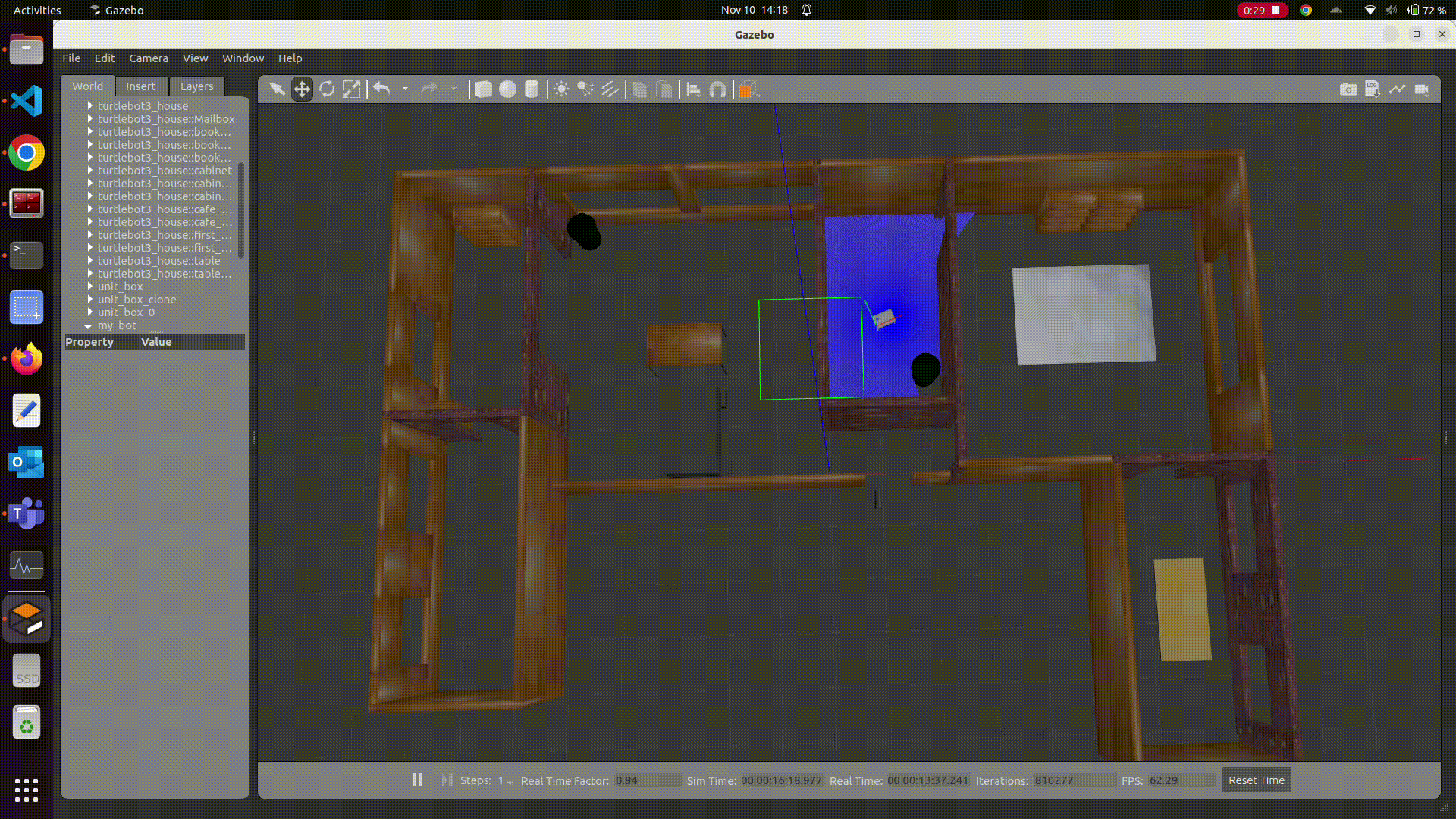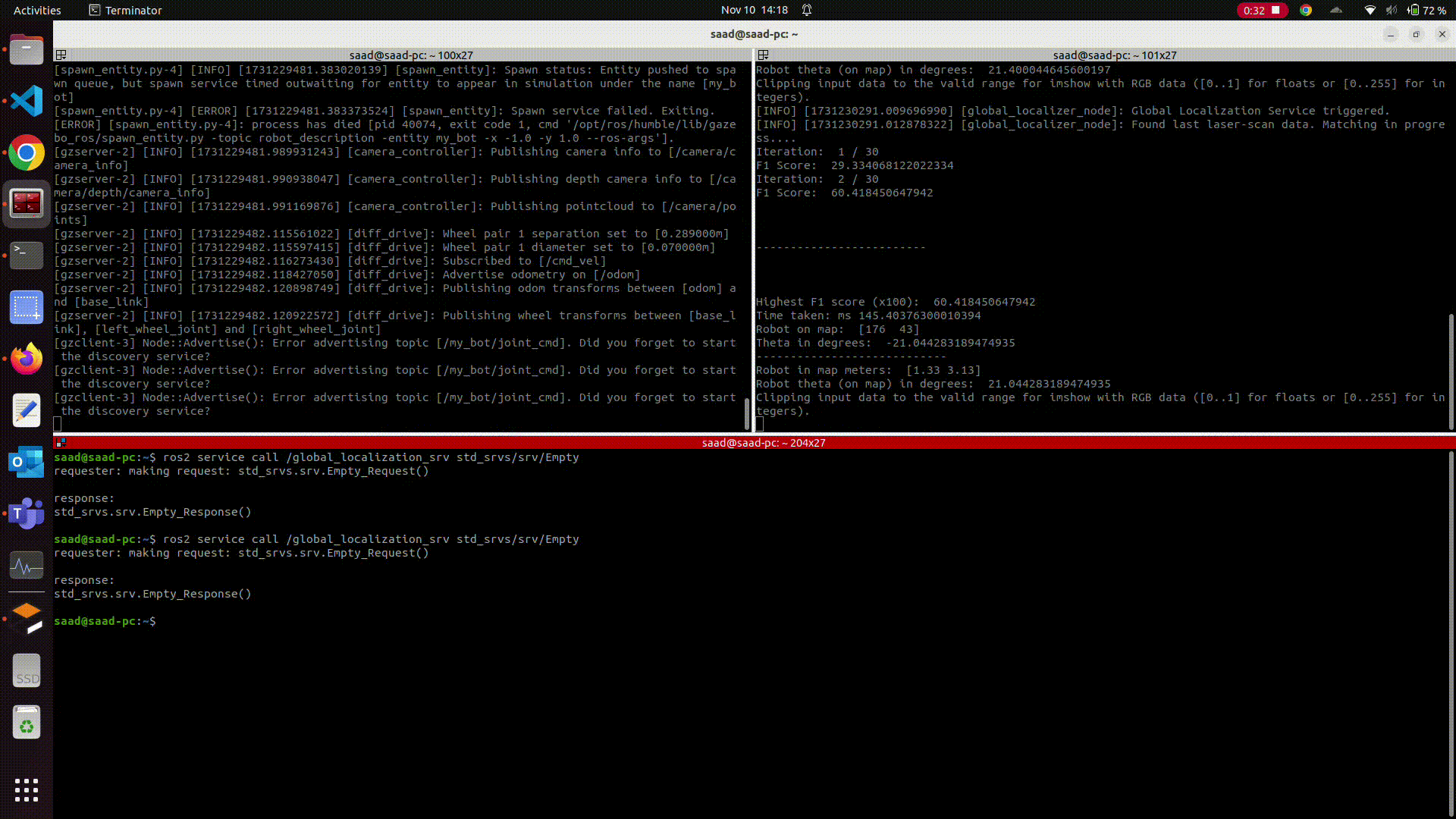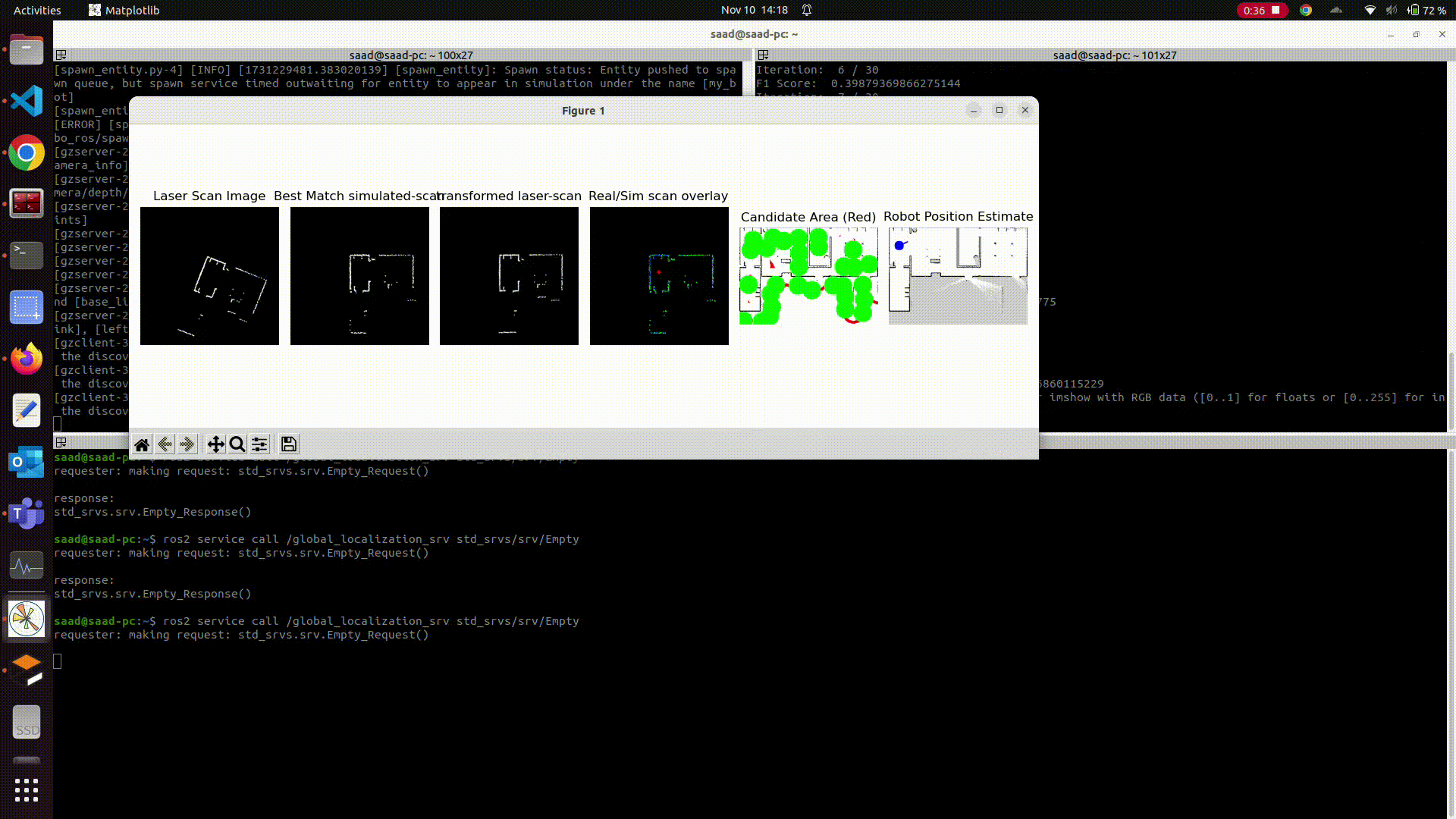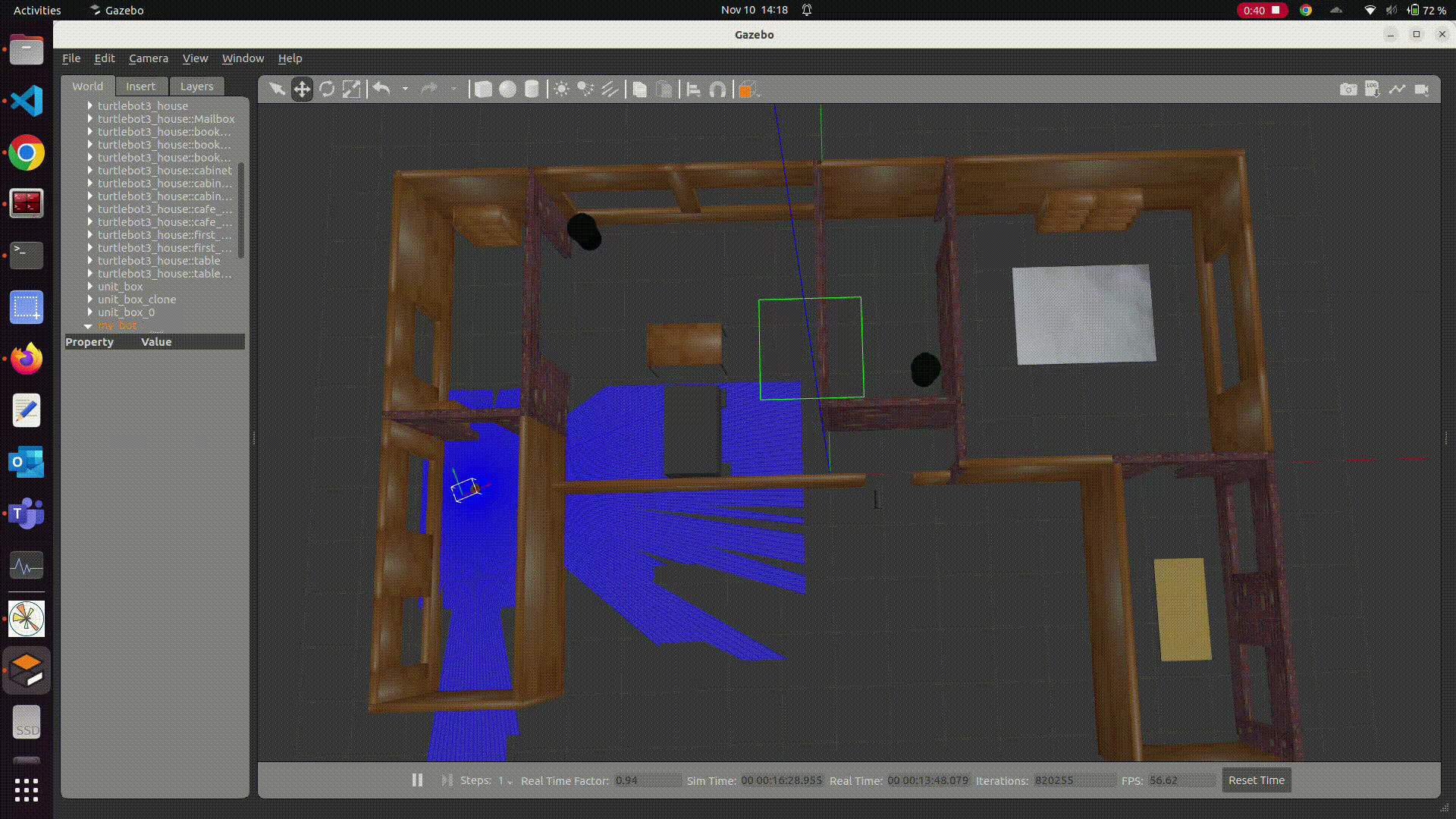
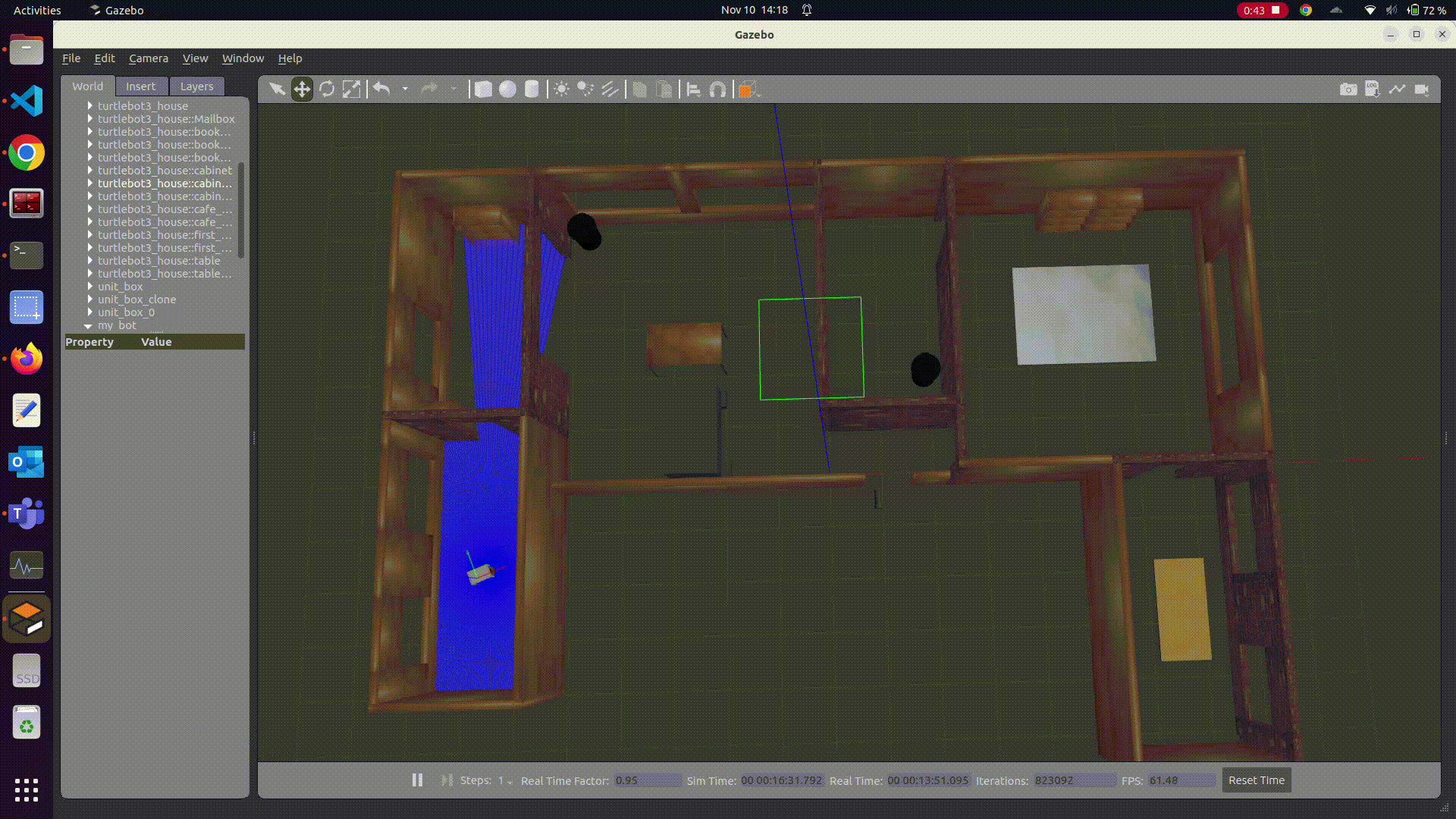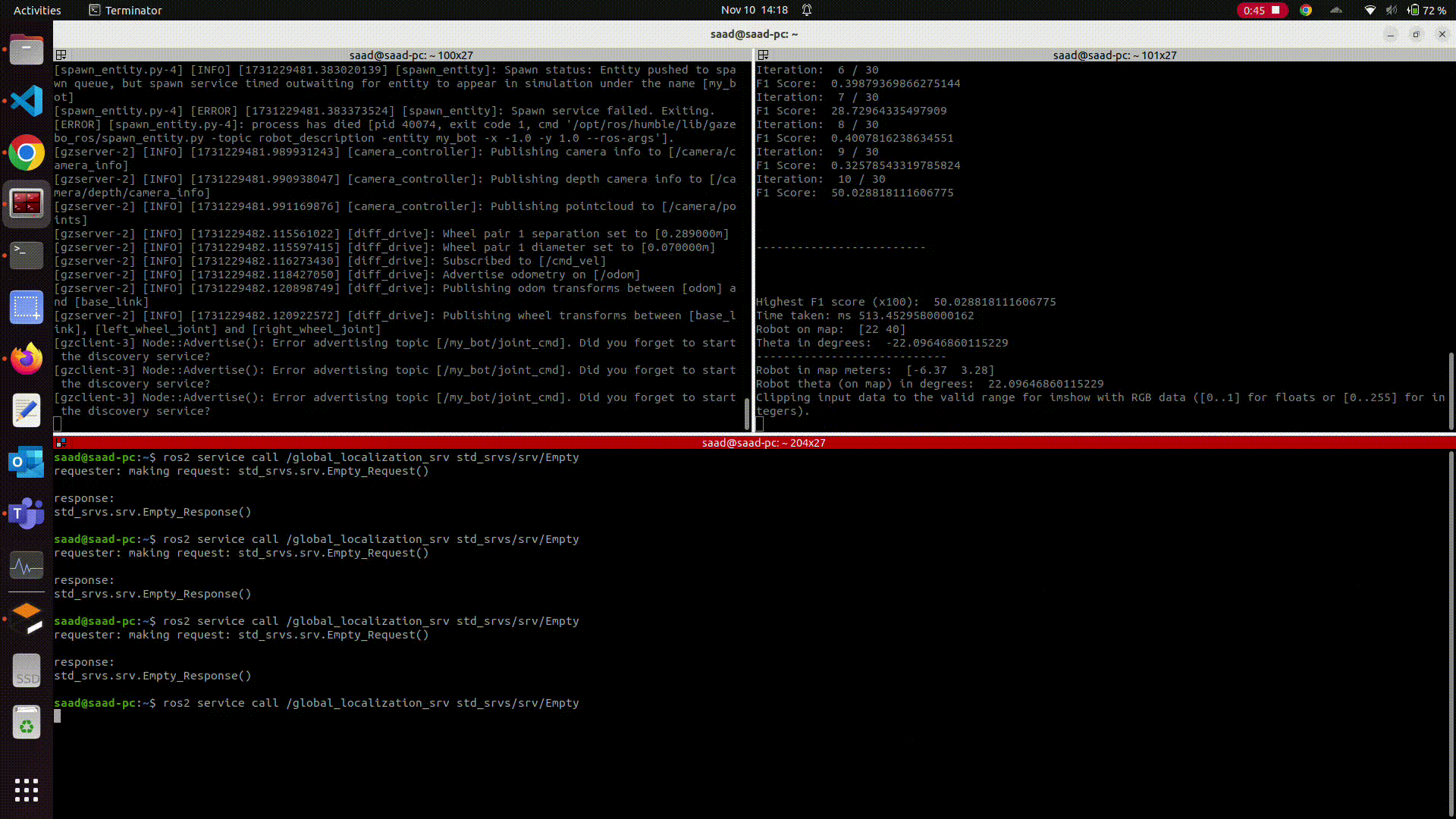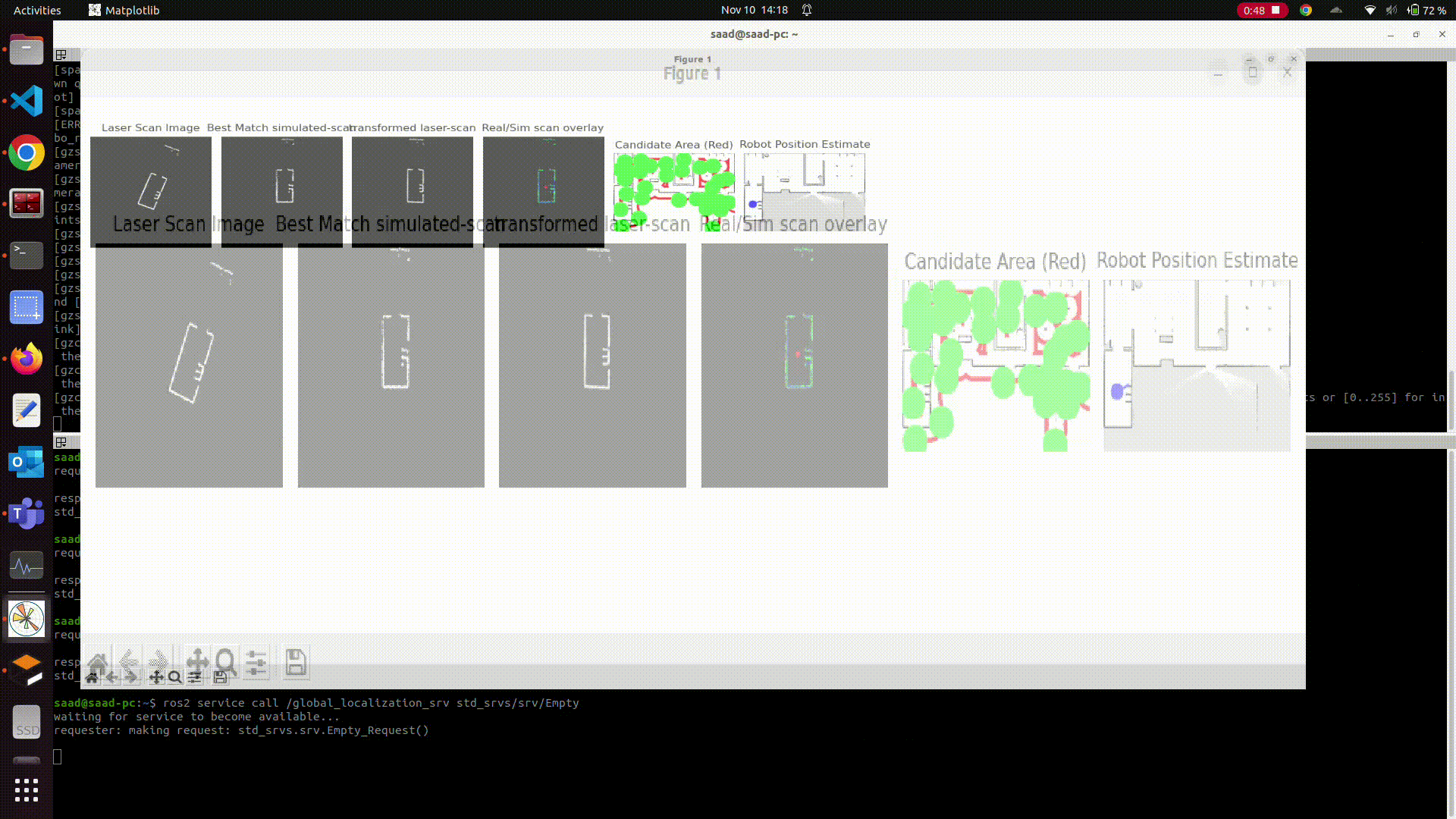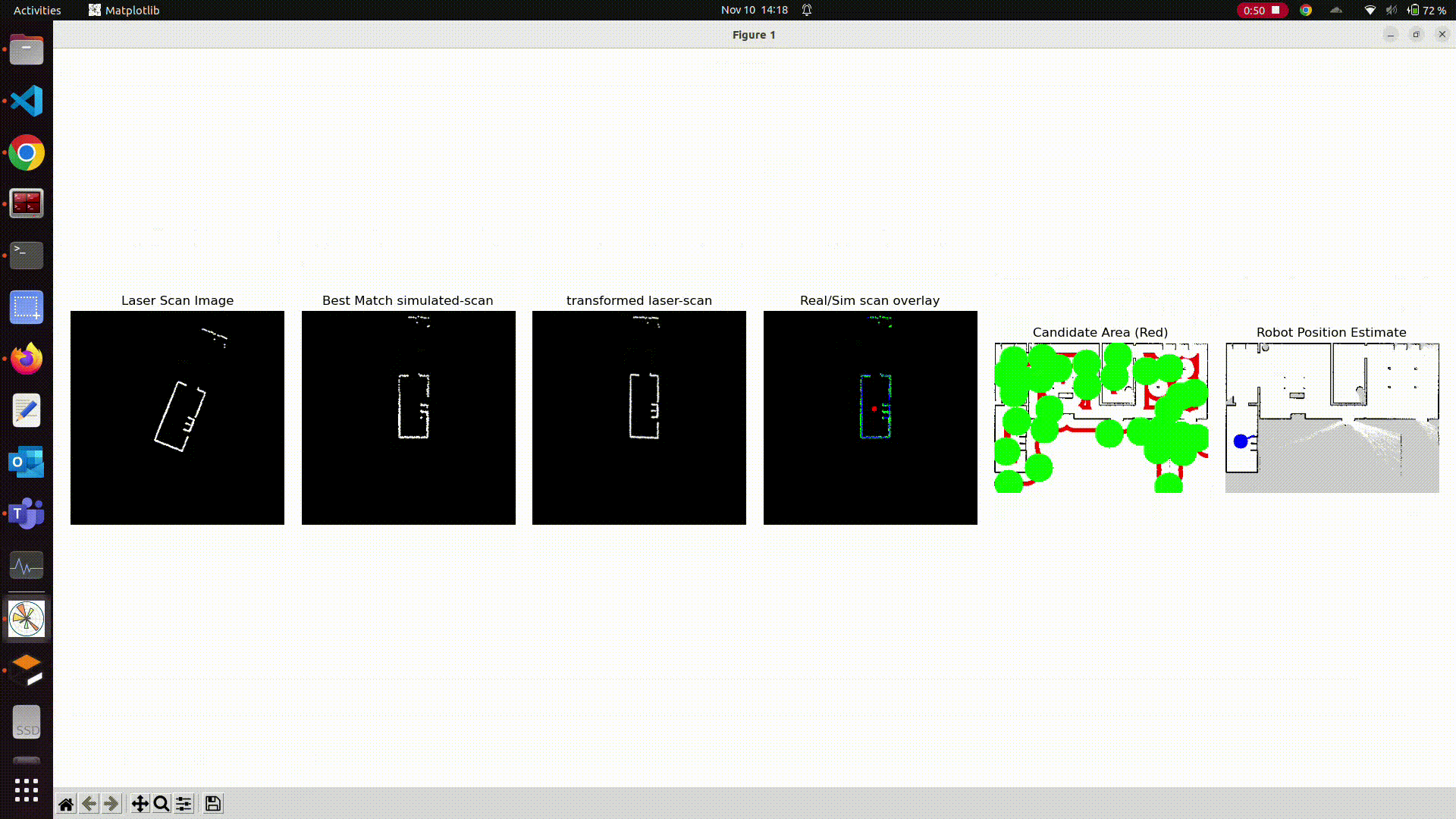
Closer look
Here is a closer look:
Robot Position
Estimated Pose
Contributing
Contributions to the Global Localizer package are welcome! If you encounter any issues or have suggestions for improvements, please open an issue on the GitHub repository.
Wiki Tutorials
Package Dependencies
| Deps | Name |
|---|---|
| ament_copyright | |
| ament_flake8 | |
| ament_pep257 |
System Dependencies
| Name |
|---|
| python3-pytest |