Repository Summary
| Description | Simulation for the Avular Origin robot |
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/avular-robotics/avular_origin_simulation.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | origin_1.0/1 |
| Last Updated | 2025-03-07 |
| Dev Status | UNKNOWN |
| CI status | No Continuous Integration |
| Released | UNRELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (0)
Good First Issues (0) Pull Requests to Review (0) |
Packages
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| origin_one_gazebo | 0.0.0 |
README
Avular Origin simulation
This repository contains the simulation environment for the Avular Origin One, using Gazebo Fortress and ROS2 Humble.
Getting started
We currently only support ROS2 Humble on Ubuntu 22.04. For installing ROS2 Humble on your system, refer to the ROS2 Humble installation guide. After making sure that ROS2 Humble is installed, install Gazebo Fortress on your system:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install ros-humble-ros-gz git-lfs
To get started with the Avular Origin Simulation, first make a ROS workspace on your computer (for instructions, see the ROS tutorial). Next, go to the ‘src’ folder of your workspace and clone this repository:
cd <your-ros-workspace>/src
git clone -b origin_1.0/1 https://github.com/avular-robotics/avular_origin_simulation.git
In the same src folder, we also need to clone the avular_origin_description repository, which contains the URDF and meshes for the Origin One robot:
git clone https://github.com/avular-robotics/avular_origin_description.git
cd avular_origin_description
git lfs pull
Finally, we can install debian packages for the cmd_vel_controller, which the real Origin One robot uses to prioritize various control command inputs.
This step is optional, but recommended if you want the simulation to behave similar to the real robot, or if you want to use Avular example code.
To do so, go to the cmd_vel_controller folder in this repository and use apt to install the binary packages:
cd <your-ros-workspace>/src/avular_origin_simulation/cmd_vel_controller/
sudo apt install ./loggercxx_3.0.0_amd64.deb ./rclcpp-avular_3.0.0_amd64.deb ./origin-msgs_1.0.0_amd64.deb ./cmd-vel-controller_1.7.1_amd64.deb
Next, go to the top level workspace folder and build the packages in the workspace:
cd <your-ros-workspace>
colcon build --symlink-install
This will generate a warning that easy_install is deprecated, which can be ignored.
You can now source the workspace (so ROS knows where to find the packages) and launch the simulation environment:
source install/setup.bash
ros2 launch origin_one_gazebo ty_test_area.launch.py use_cmd_vel_controller:=True
Note that you can set use_cmd_vel_controller to False if you don’t want to use the cmd_vel_controller package.
Alternatively, the simulation can also be launched with the mecanum wheel configuration on the robot:
ros2 launch origin_one_gazebo ty_test_area.launch.py use_cmd_vel_controller:=True drive_configuration:=mecanum_drive
This will show the avular simulation environment in Gazebo Fortress, with the Origin One spawned. You can now drag to mouse to change the view to the robot model. If you want to launch the simulation without sourcing each time, you can source the setup file in your bashrc:
echo "source <path_to_workspace>/install/setup.bash" >> ~/.bashrc
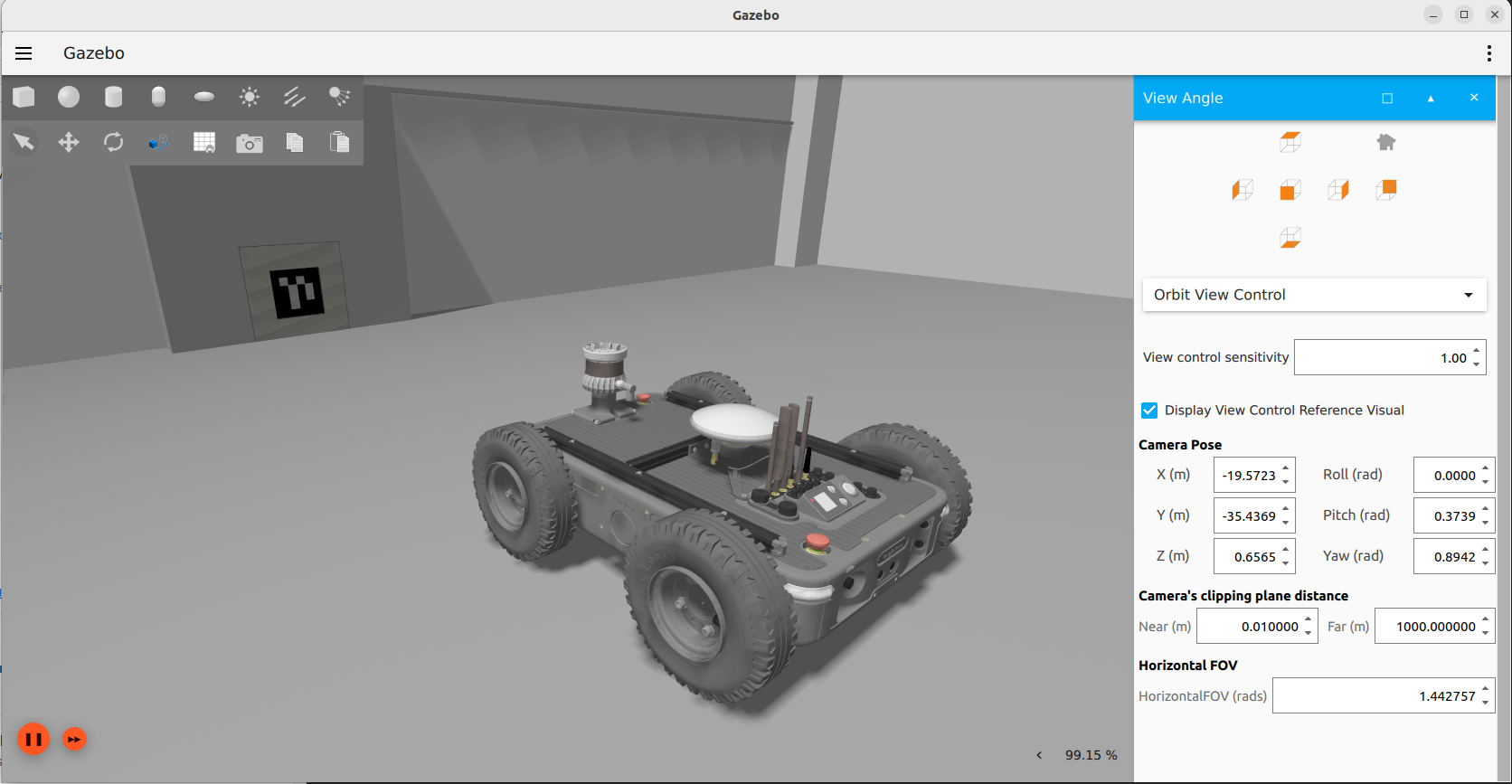
Driving and visualizing the robot in the simulation
The simulation contains gazebo plugins for the drive controller, the Ouster LiDAR and the realsense camera. To visualize the robot and its sensors, you can use the RViz visualization tool. To launch RViz with the correct configuration, run the following command:
ros2 launch origin_one_description origin_one_rviz.launch.py
This will open RViz with the robot model and the sensor data. You can now drive the robot around in the simulation by publishing Twist messages to the /robot/cmd_vel topic. For example by using the teleop_twist_keyboard package:
sudo apt install ros-humble-teleop-twist-keyboard
ros2 run teleop_twist_keyboard teleop_twist_keyboard --ros-args -r /cmd_vel:=/robot/cmd_vel
