Repository Summary
| Description | Fast LOAM: Fast and Optimized Lidar Odometry And Mapping for indoor/outdoor localization (Lidar SLAM) |
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/flynneva/floam.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | main |
| Last Updated | 2021-08-23 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| CI status | No Continuous Integration |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (0)
Good First Issues (0) Pull Requests to Review (0) |
Packages
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| floam | 0.1.0 |
README
FLOAM
Fast LOAM (Lidar Odometry And Mapping)
This work is an optimized version of A-LOAM and LOAM with the computational cost reduced by up to 3 times. This code is modified from LOAM and A-LOAM .
Modifier: Wang Han, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore
Modifier: Evan Flynn
1. Demo Highlights
Watch our demo at Video Link
2. Evaluation
2.1. Computational efficiency evaluation
Computational efficiency evaluation (based on KITTI dataset):
Platform: Intel® Core™ i7-8700 CPU @ 3.20GHz
| Dataset | ALOAM | FLOAM |
|———————————————-|—————————-|————————|
| KITTI | 151ms | 59ms |
Localization error:
| Dataset | ALOAM | FLOAM |
|———————————————-|—————————-|————————|
| KITTI sequence 00 | 0.55% | 0.51% |
| KITTI sequence 02 | 3.93% | 1.25% |
| KITTI sequence 05 | 1.28% | 0.93% |
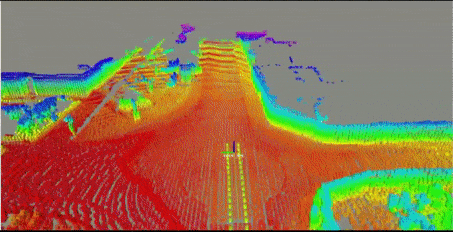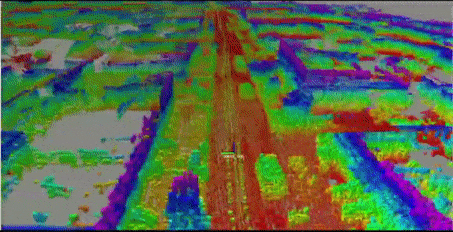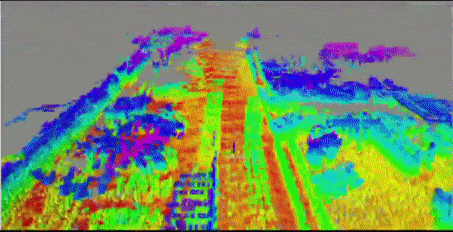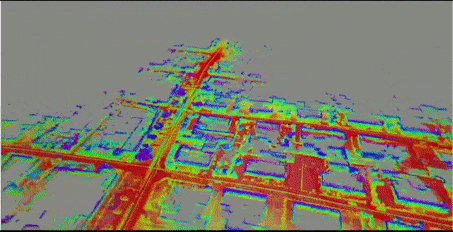
2.2. localization result
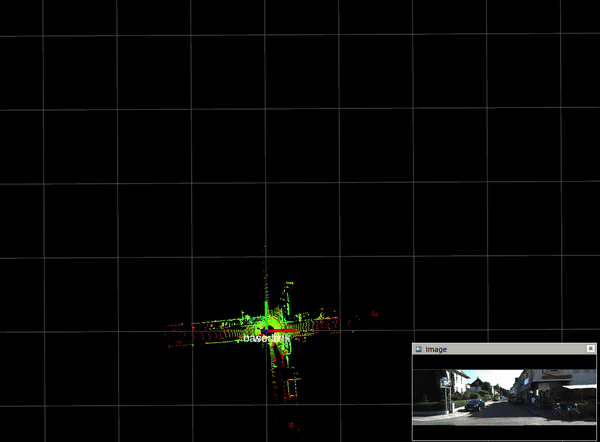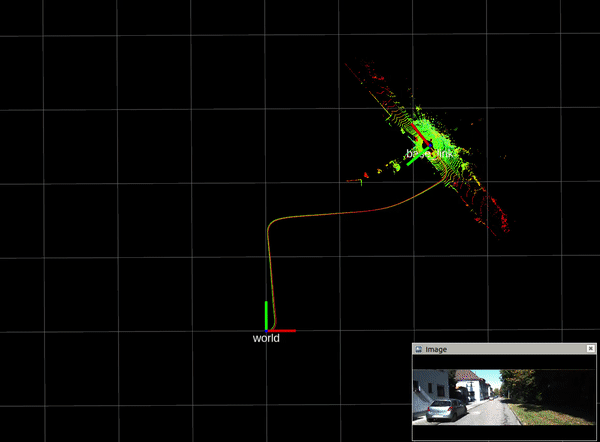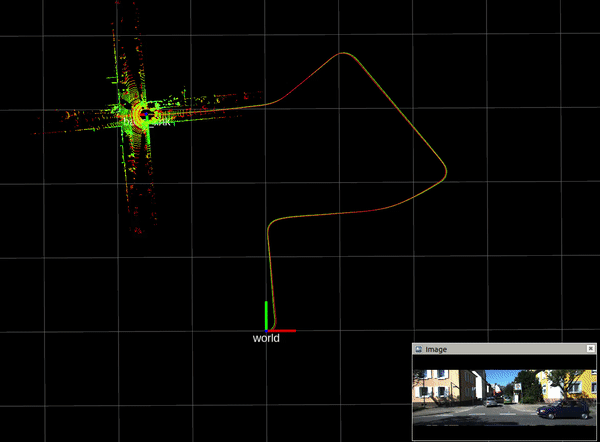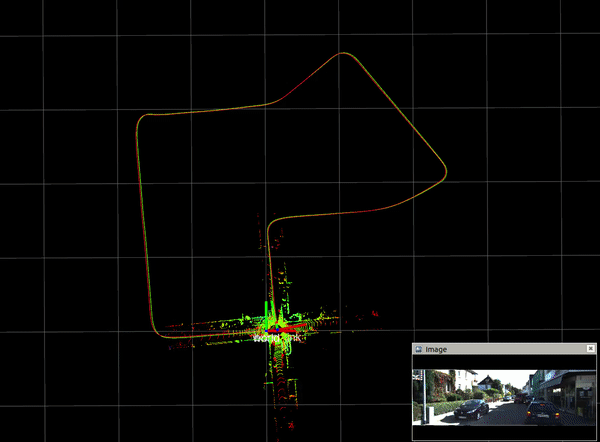
2.3. mapping result
3. Prerequisites
3.1 Ubuntu and ROS
Ubuntu 64-bit 18.04 or 20.04
ROS Melodic or Noetic. ROS Installation
3.2. **Install dependencies using rosdep
Install dependencies using rosdep:
cd /your/catkin_ws
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -y
Or you can manually install the dependencies below:
3.3. Ceres Solver
Follow Ceres Installation.
3.4. PCL
Follow PCL Installation.
3.5. Trajectory visualization
For visualization purpose, this package uses hector trajectory sever, you may install the package by
sudo apt-get install ros-melodic-hector-trajectory-server
Alternatively, you may remove the hector trajectory server node if trajectory visualization is not needed
4. Build
Make sure to have installed the required dependencies as above before trying to build this package.
4.1 Clone repository:
cd ~/catkin_ws/src
git clone https://github.com/wh200720041/floam.git
cd ..
catkin_make
source ~/catkin_ws/devel/setup.bash
4.2 Download test rosbag
Download KITTI sequence 05 or KITTI sequence 07
Unzip compressed file 2011_09_30_0018.zip. If your system does not have unzip. please install unzip by
sudo apt-get install unzip
And this may take a few minutes to unzip the file
cd ~/Downloads
unzip ~/Downloads/2011_09_30_0018.zip
4.3 Launch ROS
roslaunch floam floam.launch
if you would like to create the map at the same time, you can run (more cpu cost)
roslaunch floam floam_mapping.launch
If the mapping process is slow, you may wish to change the rosbag speed by replacing “–clock -r 0.5” with “–clock -r 0.2” in your launch file, or you can change the map publish frequency manually (default is 10 Hz)
4.4 How to use floam nodes
The floam package provides three nodes: floam_lidar_node, floam_odom_node, floam_mapping_node. Each of these nodes feeds the next with the proper data, so the data flow goes:
-
floam_lidar_node: detects edges and surfaces of input pointcloud -
floam_odom_node: estimate odometery based on edges and surfaces -
floam_mapping_node: combine pointcloud into map using odom estimation
Each node could be ran without the others, however the inputs of each need to be satisifed in order to run properly.
For example, the floam_mapping_node could be used with any odometry estimation and only requires an odom topic and a pointcloud topic. The odom topic could be coming from robot_localization or some other source for example.
5. Test on other sequence
To generate rosbag file of kitti dataset, you may use the tools provided by kitti_to_rosbag or kitti2bag
The default settings in the main launch file floam_all.launch should be set for this recording. See below for instructions on how to adjust the parameters for more fine-tuned performance
6. The Nodes of floam
The floam package was written in a way to be adjustable and usable for most lidars on the market today. Below is an outline of the parameters that you can adjust to see fine-tune the performance of floam for your device and use-case.
There are three main nodes normally run at once: floam_lidar_node, floam_odom_node and floam_mapping_node. Each one serves a specific purpose and can be ran without the other if needed. The adjustable parameters for each are outlined below.
6.1 floam_lidar_node
The floam_lidar_node has one primary purpose and that is to consume a single points_topic and detect edges and surfaces within the pointcloud. Within the node there are many paramters you can adjust to fine-tune this detection process for your use-case.
There are two different flavors of the lidar node for more efficient processing techniques for organized and unorganized pointclouds.
6.1.1. common parameters
-
points_topic: the raw input pointcloud -
lidar_frame_id: the frame_id for your lidar (should be the same one that is in the header of yourpoints_topic) -
frame_id: new frame_id for edge and surface pointclouds. -
edge_threshold: the threshold of curfavature of a surface to classify it as an edge. A larger edge threshold means more points will be classified as surfaces (seeline 156insrc/lidar.cppfor use). -
min_distance: ignore points within this distance -
max_distance: ignore points past this distance
6.1.2 scanning lidar parameters
-
scan_lines: number of scan lines in the device (i.e. velodyne, ouster types). if you set this value to1then a kdTree is used to search for neighboring points within a radius (TODO: implement k point search method). -
skip_points: used as an incrementor to decide which points to run the edge detection (kdTree search) on. Essentially “skipping” the number of points specified (i.e. ifskip_pointsis 10, kdTree search will be performed on points 0, 10, 20, etc. in original pointcloud). -
search_radius: used inkdTree.radiusSearchfunction to find all points around a specified point within some radius (meters).
[NOT YET USED]
-
search_k: used in kdTree search to find k nearset points to specified point. -
period: period of sensor scan (not used anymore)
6.1.3 imaging lidar parameters
- TODO
6.2 floam_odom_node parameters
-
odom_parent_frame_id: the parent frame of the odometry estimation, defaults tomap. -
edge_cloud_topic: the input pointcloud with labeled edges -
surface_cloud_topic: the input pointcloud wiht labeled surfaces
6.3 floam_mapping_node parameters
-
map_resolution: defines the resolution of the final map pointcloud (meters) -
mapping_points_topic: input pointcloud to create map from -
mapping_odom_topic: input odom to use to create map -
output_map_topic: output map pointcloud topic
7.Acknowledgements
Thanks for A-LOAM and LOAM(J. Zhang and S. Singh. LOAM: Lidar Odometry and Mapping in Real-time) and LOAM_NOTED.
CONTRIBUTING
Repository Summary
| Description | Fast LOAM: Fast and Optimized Lidar Odometry And Mapping for indoor/outdoor localization (Lidar SLAM) |
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/flynneva/floam.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | main |
| Last Updated | 2021-08-23 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| CI status | No Continuous Integration |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (0)
Good First Issues (0) Pull Requests to Review (0) |
Packages
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| floam | 0.1.0 |
README
FLOAM
Fast LOAM (Lidar Odometry And Mapping)
This work is an optimized version of A-LOAM and LOAM with the computational cost reduced by up to 3 times. This code is modified from LOAM and A-LOAM .
Modifier: Wang Han, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore
Modifier: Evan Flynn
1. Demo Highlights
Watch our demo at Video Link
2. Evaluation
2.1. Computational efficiency evaluation
Computational efficiency evaluation (based on KITTI dataset):
Platform: Intel® Core™ i7-8700 CPU @ 3.20GHz
| Dataset | ALOAM | FLOAM |
|———————————————-|—————————-|————————|
| KITTI | 151ms | 59ms |
Localization error:
| Dataset | ALOAM | FLOAM |
|———————————————-|—————————-|————————|
| KITTI sequence 00 | 0.55% | 0.51% |
| KITTI sequence 02 | 3.93% | 1.25% |
| KITTI sequence 05 | 1.28% | 0.93% |
2.2. localization result

2.3. mapping result
3. Prerequisites
3.1 Ubuntu and ROS
Ubuntu 64-bit 18.04 or 20.04
ROS Melodic or Noetic. ROS Installation
3.2. **Install dependencies using rosdep
Install dependencies using rosdep:
cd /your/catkin_ws
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -y
Or you can manually install the dependencies below:
3.3. Ceres Solver
Follow Ceres Installation.
3.4. PCL
Follow PCL Installation.
3.5. Trajectory visualization
For visualization purpose, this package uses hector trajectory sever, you may install the package by
sudo apt-get install ros-melodic-hector-trajectory-server
Alternatively, you may remove the hector trajectory server node if trajectory visualization is not needed
4. Build
Make sure to have installed the required dependencies as above before trying to build this package.
4.1 Clone repository:
cd ~/catkin_ws/src
git clone https://github.com/wh200720041/floam.git
cd ..
catkin_make
source ~/catkin_ws/devel/setup.bash
4.2 Download test rosbag
Download KITTI sequence 05 or KITTI sequence 07
Unzip compressed file 2011_09_30_0018.zip. If your system does not have unzip. please install unzip by
sudo apt-get install unzip
And this may take a few minutes to unzip the file
cd ~/Downloads
unzip ~/Downloads/2011_09_30_0018.zip
4.3 Launch ROS
roslaunch floam floam.launch
if you would like to create the map at the same time, you can run (more cpu cost)
roslaunch floam floam_mapping.launch
If the mapping process is slow, you may wish to change the rosbag speed by replacing “–clock -r 0.5” with “–clock -r 0.2” in your launch file, or you can change the map publish frequency manually (default is 10 Hz)
4.4 How to use floam nodes
The floam package provides three nodes: floam_lidar_node, floam_odom_node, floam_mapping_node. Each of these nodes feeds the next with the proper data, so the data flow goes:
-
floam_lidar_node: detects edges and surfaces of input pointcloud -
floam_odom_node: estimate odometery based on edges and surfaces -
floam_mapping_node: combine pointcloud into map using odom estimation
Each node could be ran without the others, however the inputs of each need to be satisifed in order to run properly.
For example, the floam_mapping_node could be used with any odometry estimation and only requires an odom topic and a pointcloud topic. The odom topic could be coming from robot_localization or some other source for example.
5. Test on other sequence
To generate rosbag file of kitti dataset, you may use the tools provided by kitti_to_rosbag or kitti2bag
The default settings in the main launch file floam_all.launch should be set for this recording. See below for instructions on how to adjust the parameters for more fine-tuned performance
6. The Nodes of floam
The floam package was written in a way to be adjustable and usable for most lidars on the market today. Below is an outline of the parameters that you can adjust to see fine-tune the performance of floam for your device and use-case.
There are three main nodes normally run at once: floam_lidar_node, floam_odom_node and floam_mapping_node. Each one serves a specific purpose and can be ran without the other if needed. The adjustable parameters for each are outlined below.
6.1 floam_lidar_node
The floam_lidar_node has one primary purpose and that is to consume a single points_topic and detect edges and surfaces within the pointcloud. Within the node there are many paramters you can adjust to fine-tune this detection process for your use-case.
There are two different flavors of the lidar node for more efficient processing techniques for organized and unorganized pointclouds.
6.1.1. common parameters
-
points_topic: the raw input pointcloud -
lidar_frame_id: the frame_id for your lidar (should be the same one that is in the header of yourpoints_topic) -
frame_id: new frame_id for edge and surface pointclouds. -
edge_threshold: the threshold of curfavature of a surface to classify it as an edge. A larger edge threshold means more points will be classified as surfaces (seeline 156insrc/lidar.cppfor use). -
min_distance: ignore points within this distance -
max_distance: ignore points past this distance
6.1.2 scanning lidar parameters
-
scan_lines: number of scan lines in the device (i.e. velodyne, ouster types). if you set this value to1then a kdTree is used to search for neighboring points within a radius (TODO: implement k point search method). -
skip_points: used as an incrementor to decide which points to run the edge detection (kdTree search) on. Essentially “skipping” the number of points specified (i.e. ifskip_pointsis 10, kdTree search will be performed on points 0, 10, 20, etc. in original pointcloud). -
search_radius: used inkdTree.radiusSearchfunction to find all points around a specified point within some radius (meters).
[NOT YET USED]
-
search_k: used in kdTree search to find k nearset points to specified point. -
period: period of sensor scan (not used anymore)
6.1.3 imaging lidar parameters
- TODO
6.2 floam_odom_node parameters
-
odom_parent_frame_id: the parent frame of the odometry estimation, defaults tomap. -
edge_cloud_topic: the input pointcloud with labeled edges -
surface_cloud_topic: the input pointcloud wiht labeled surfaces
6.3 floam_mapping_node parameters
-
map_resolution: defines the resolution of the final map pointcloud (meters) -
mapping_points_topic: input pointcloud to create map from -
mapping_odom_topic: input odom to use to create map -
output_map_topic: output map pointcloud topic
7.Acknowledgements
Thanks for A-LOAM and LOAM(J. Zhang and S. Singh. LOAM: Lidar Odometry and Mapping in Real-time) and LOAM_NOTED.