
|
int-ball2_isaac_sim repositoryrobotics iss ros space-robotics isaac-sim space-ros int-ball2 int-ball2_control int-ball2_isaac_sim |
|
|
Repository Summary
| Description | Int-Ball2 Simulator (Isaac Sim) |
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/sd-robotics/int-ball2_isaac_sim.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | main |
| Last Updated | 2025-03-25 |
| Dev Status | UNKNOWN |
| CI status | No Continuous Integration |
| Released | UNRELEASED |
| Tags | robotics iss ros space-robotics isaac-sim space-ros int-ball2 |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (0)
Good First Issues (0) Pull Requests to Review (0) |
Packages
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| int-ball2_control | 0.0.0 |
| int-ball2_isaac_sim | 0.0.0 |
README
Int-Ball2 Simulator (Isaac Sim)









Table of Contents
What is Int-Ball2 Simulator (Isaac Sim)
Int-Ball2 is a free-flying camera robot deployed in the ISS Japan Experimental Module (JEM). It is remotely controlled from the ground to capture video images and support astronauts. Additionally, Int-Ball2 can run user-developed software as an extended functionality and can be used as a platform for demonstrating robotic technology in space.
This repository provides ROS tools and a NVIDIA Isaac Sim simulator environment of Int-Ball2. It simulates Int-Ball2’s behavior in the ISS/JEM environment allowing user-developed programs to be tested.

Prerequisites
In order to use this project, you need to get ready the following environment.
| Package | Version |
|---|---|
| Ubuntu | 22.04 (Jammy Jellyfish) |
| Isaac Sim | 4.2.0 (September 2024) |
| ROS | Humble Hawksbill |
| Python | 3.10 <= |
Installation
Clone Repository
Make a workspace if you do not have one already.
mkdir -p ~/int-ball2_ws/src
cd ~/int-ball2_ws/src
Clone this package into your workspace.
git clone https://github.com/sd-robotics/int-ball2_isaac_sim.git
Install Dependencies
Move into your workspace.
cd ~/int-ball2_ws/
Install the dependencies.
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
Download Assets
Move into this project folder.
cd ~/int-ball2_ws/src/int-ball2_isaac_sim
Download the assets (Int-Ball2, JEM, etc).
bash install_local.sh
Usage
Build & Source
Build this package and source your workspace.
cd ~/int-ball2_ws
colcon build --symlink-install
source install/setup.bash
Launch the Simulator
Launch the simulation by ros2 launch.
ros2 launch int-ball2_isaac_sim int-ball2_isaac_sim.launch.py gui:="~/int-ball2_ws/src/int-ball2_isaac_sim/assets/KIBOU.usd"
[!NOTE] If no
ROS_DOMAIN_IDis set, ID0will be used as default value.
In order to start the Isaac Sim simulation you need to press the “▶” button on the left side of the screen. Then ROS bridge will run in Isaac Sim and make possible the connection with Int-Ball2 sensors and propulsion systems.
You can also change the perspective to look around the ISS Kibo (Japanese Experiment Module) environment.
[!TIP] If you are using laptop to run Isaac Sim and suffering the problem of monitor freezing when Isaac Sim is launched, you might want to switch the system to use the NVIDIA GPU by the following command.
sudo prime-select nvidiaThis will result in a better performance in graphic-intensive tasks. To check if your laptop has successfully switched to NVIDIA GPU, you can use the command.
prime-select query
Feedback from ROS Bridge
The following data can be obtained by the user program.
| Type | ROS Definition Name | Overview |
|---|---|---|
| Topic | /camera_main/image_raw | Image of the main camera on the front of the Int-Ball2. |
| Topic | /camera_main/camera_info | Information about the main camera on the front of Int-Ball2. |
| Topic | /camera_left/image_raw | Image of the stereo camera on the left side of Int-Ball2 (left). |
| Topic | /camera_left/camera_info | Information on the stereo camera on the left side of Int-Ball2 (left). |
| Topic | /camera_right/image_raw | Image of the stereo camera on the left side of Int-Ball2 (right). |
| Topic | /camera_right/camera_info | Information on the stereo camera on the left side of Int-Ball2 (right). |
| Topic | /imu/imu | Sensor value of the IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit). |
| Topic | /ground_truth | True value of the robot position and orientation (docking station to Int-Ball2 body). |
The following data can be controlled by the user program.
| Type | ROS Definition Name | Overview |
|---|---|---|
| Topic | /ctl/wrench | Input values of the force and torque applied to Int-Ball2. |
Teleoperation (Joy Controller)
Source your workspace.
cd ~/int-ball2_ws
source install/setup.bash
Make sure that you have a controller (such as DualShock4) connected to the PC before running the command. Then run the teleop launcher.
ros2 launch int-ball2_control int-ball2_teleop.launch.py
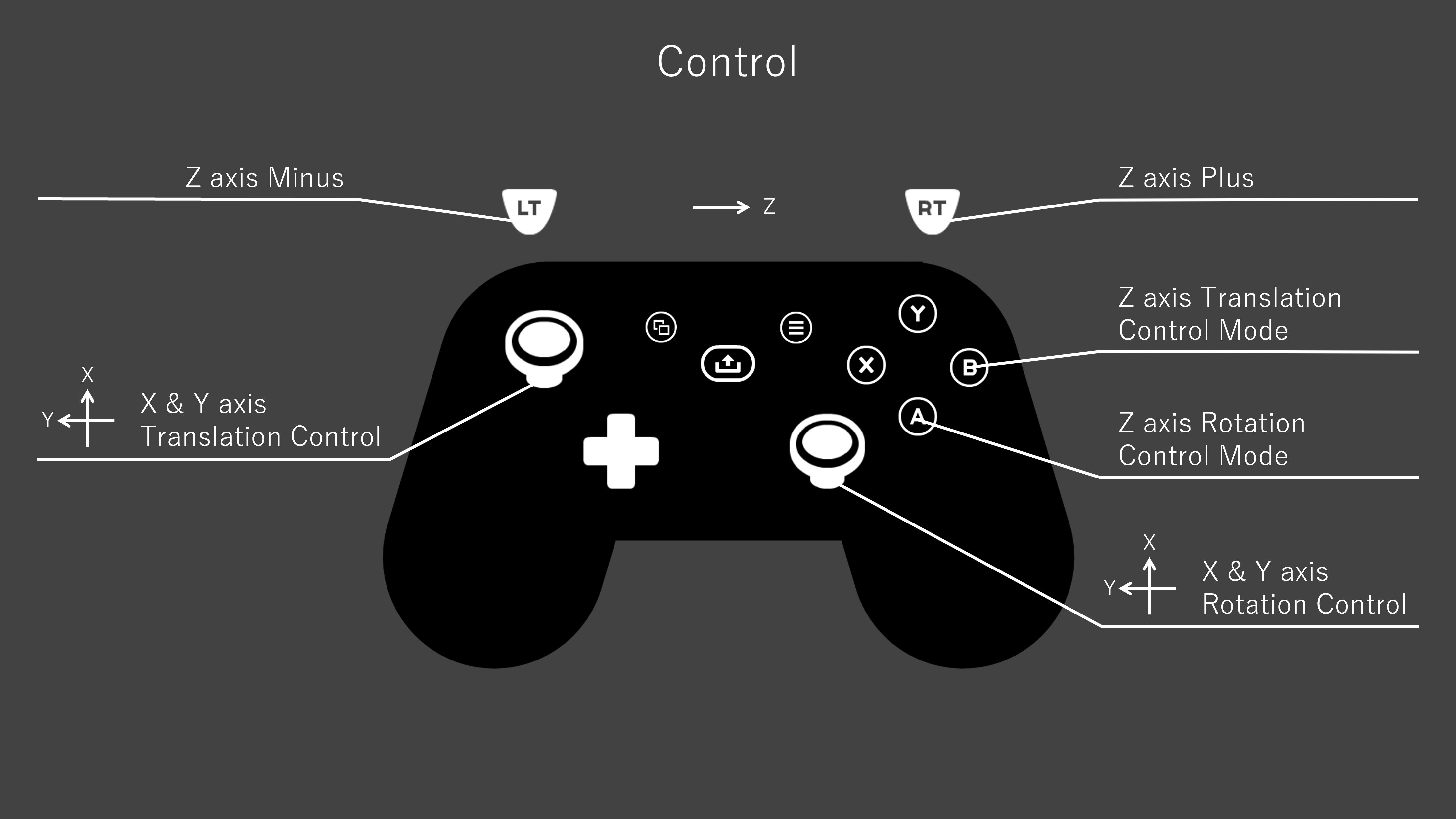
Operation with the controller is as follows.
For translational movement:
- Left stick for X-axis and Y-axis,
- B button + RT or LT for Z-axis.
For rotational movement:
- Right stick for X-axis and Y-axis,
- A button + RT or LT for Z-axis.
Data Visualization
Source your workspace.
cd ~/int-ball2_ws
source install/setup.bash
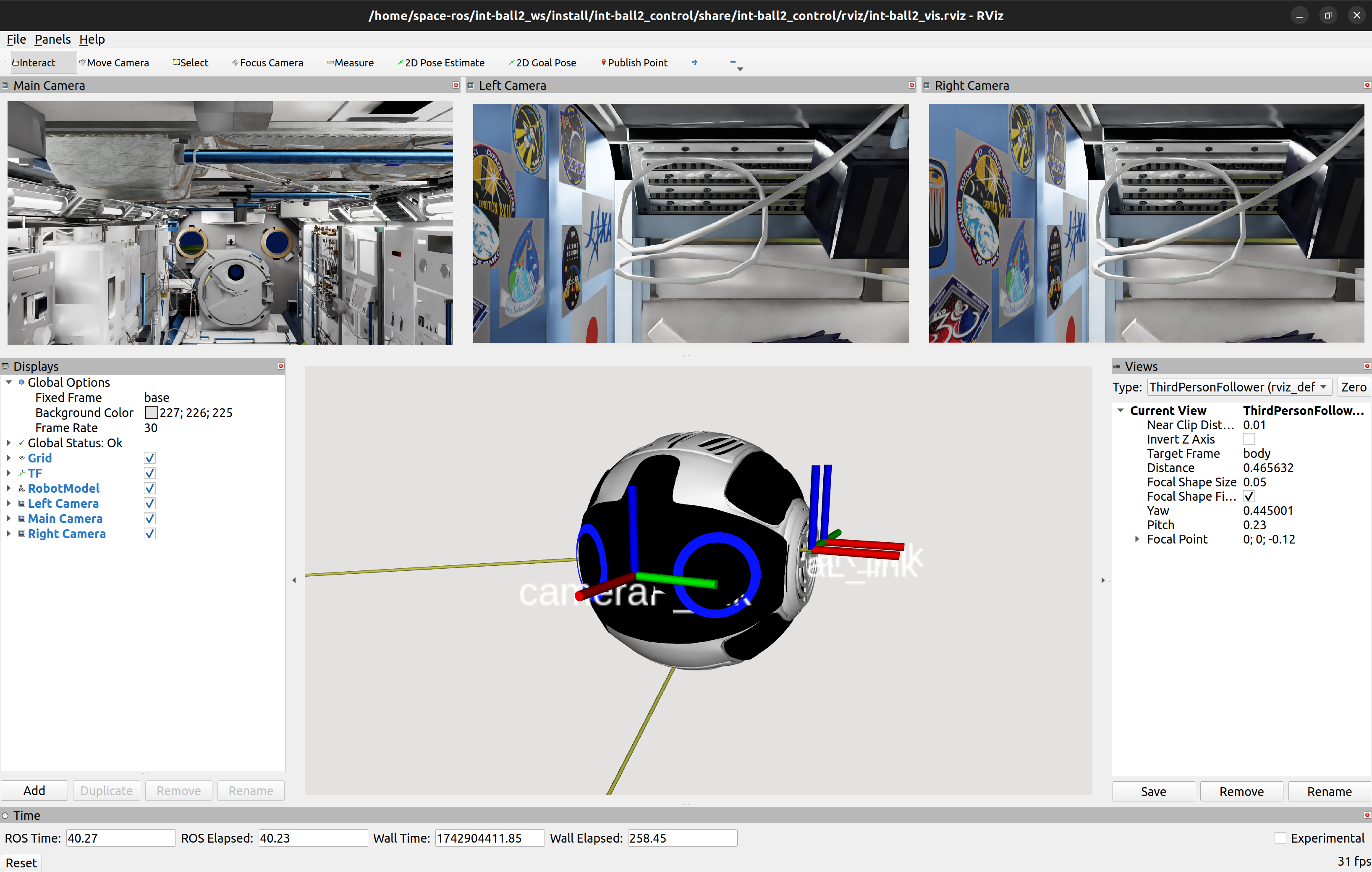
Launch Rviz to visualize the obtained data.
ros2 launch int-ball2_control rviz_visualize.launch.py
Acknowledgement
This simulator was developed by Space Data Inc. in cooperation with JAXA within the framework of the Space Innovation Partnership (J-SPARC: JAXA Space Innovation through Partnership and Co-creation).
[!TIP] This document includes content from JAXA’s Int-Ball2 Simulator, which is licensed under the Apache License 2.0.


