
|
navrl repositoryreinforcement-learning robotics collision-avoidance robot-navigation nvidia-isaac embodied-ai isaac-sim ros1-noetic ros2-humble |
|
|

|
navrl repositoryreinforcement-learning robotics collision-avoidance robot-navigation nvidia-isaac embodied-ai isaac-sim ros1-noetic ros2-humble |
|
|

|
navrl repositoryreinforcement-learning robotics collision-avoidance robot-navigation nvidia-isaac embodied-ai isaac-sim ros1-noetic ros2-humble |
|
|

|
navrl repositoryreinforcement-learning robotics collision-avoidance robot-navigation nvidia-isaac embodied-ai isaac-sim ros1-noetic ros2-humble |
|
|

|
navrl repositoryreinforcement-learning robotics collision-avoidance robot-navigation nvidia-isaac embodied-ai isaac-sim ros1-noetic ros2-humble map_manager navigation_runner onboard_detector uav_simulator |
|
|
Repository Summary
| Description | [IEEE RA-L'25] NavRL: Learning Safe Flight in Dynamic Environments (NVIDIA Isaac/Python/ROS1/ROS2) |
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/zhefan-xu/navrl.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | main |
| Last Updated | 2025-05-11 |
| Dev Status | UNMAINTAINED |
| CI status | No Continuous Integration |
| Released | UNRELEASED |
| Tags | reinforcement-learning robotics collision-avoidance robot-navigation nvidia-isaac embodied-ai isaac-sim ros1-noetic ros2-humble |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (0)
Good First Issues (0) Pull Requests to Review (0) |
Packages
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| map_manager | 1.0.0 |
| navigation_runner | 1.0.0 |
| onboard_detector | 1.0.0 |
| uav_simulator | 1.0.0 |
README
NavRL: Learning Safe Flight in Dynamic Environments
Welcome to the NavRL repository! This repository provides the implementation of the NavRL framework, designed to enable robots to safely navigate dynamic environments using Reinforcement Learning. While the original paper focuses on UAV navigation, the NavRL can be extended to any robot that adopts a velocity-based control system.
 |
 |
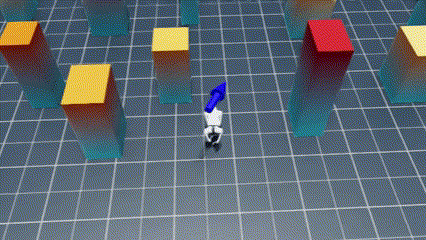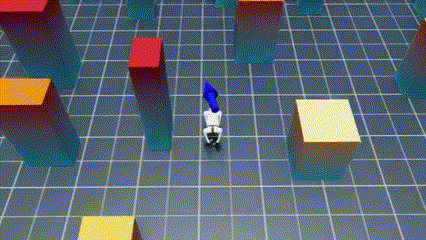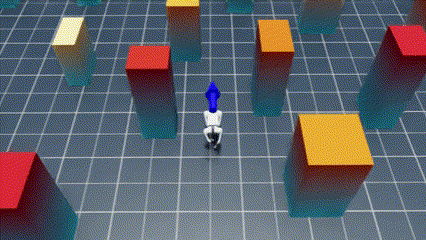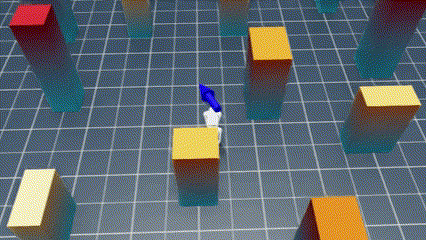 |
For additional details, please refer to the related paper available here:
Zhefan Xu, Xinming Han, Haoyu Shen, Hanyu Jin, and Kenji Shimada, “NavRL: Learning Safe Flight in Dynamic Environments”, IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters (RA-L), 2025. [IEEE Xplore] [preprint] [YouTube] [BiliBili]
News
- 2025-04-06: We release easy-to-run Python scripts that allows users to quickly run demos.
- 2025-02-23: The GitHub code, video demos, and relavant papers for our NavRL framework are released. The authors will actively maintain and update this repo!
Table of Contents
- Training in NVIDIA Isaac Sim
- Deployment Virtual Environment
- NavRL ROS1 Deployment
- NavRL ROS2 Deployment
- Citation and Reference
- Acknowledgement
NavRL Quick Demos in 3 Minutes
We provide a pretrained model and easy-to-run Python scripts for quick demos of the NavRL framework.
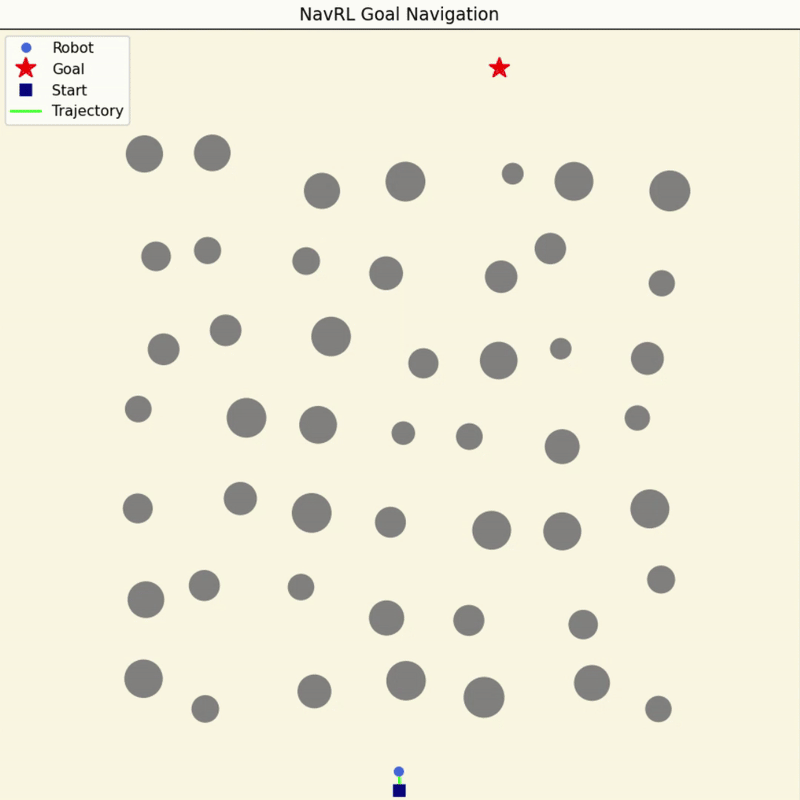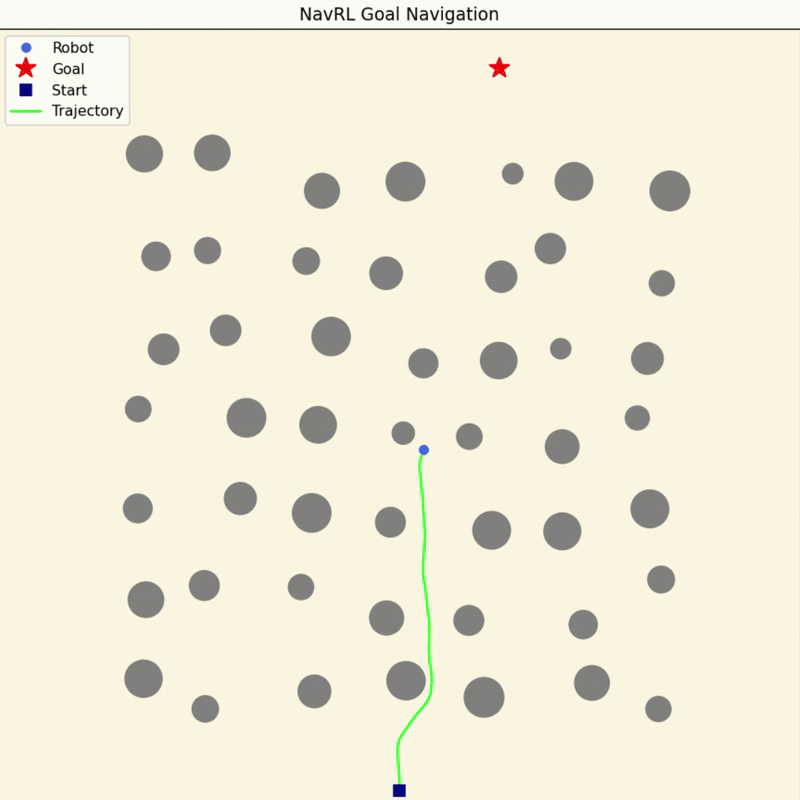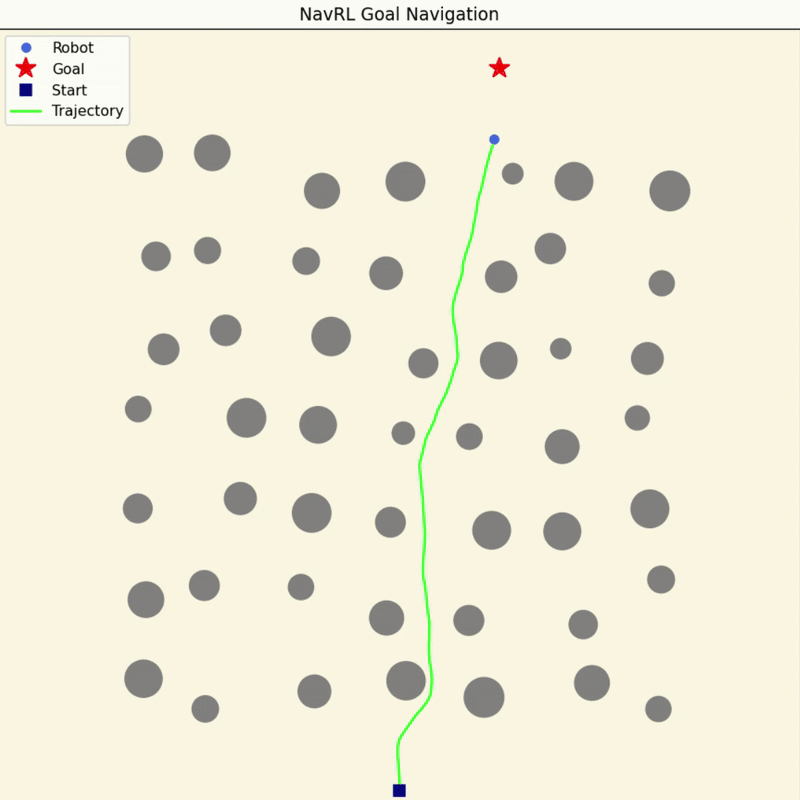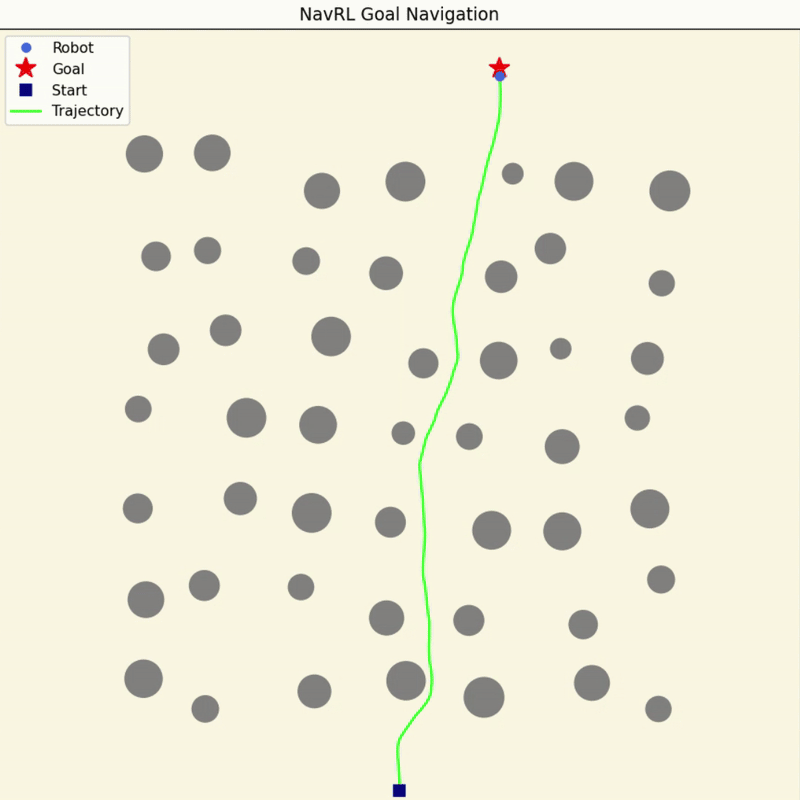 |
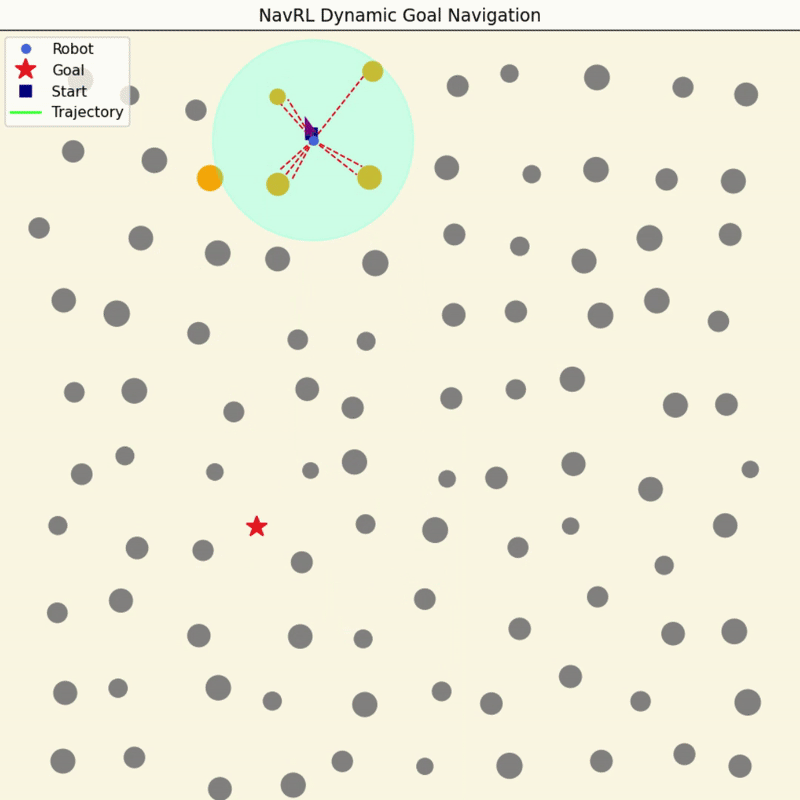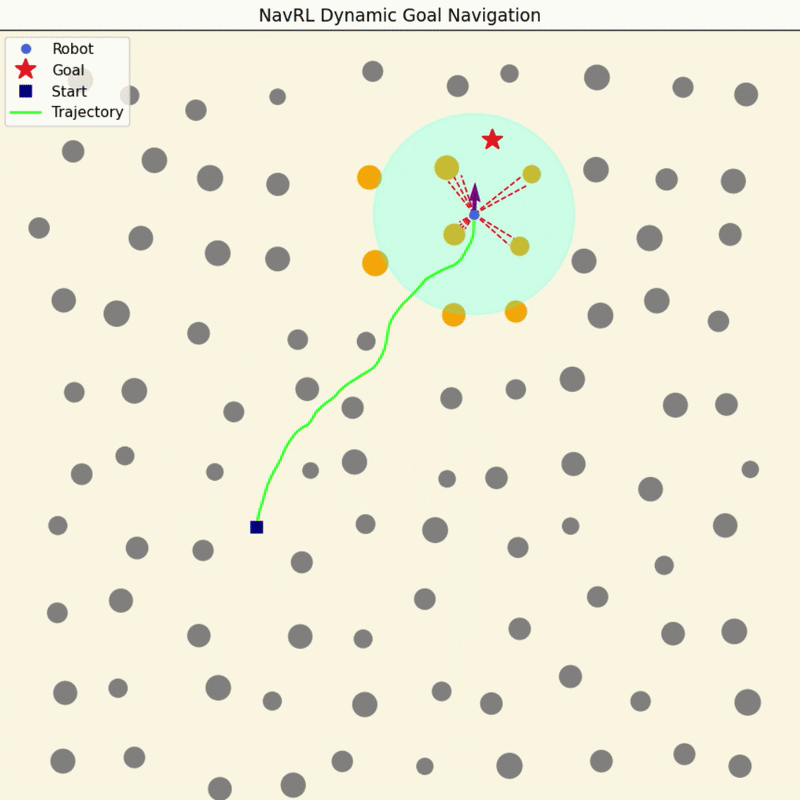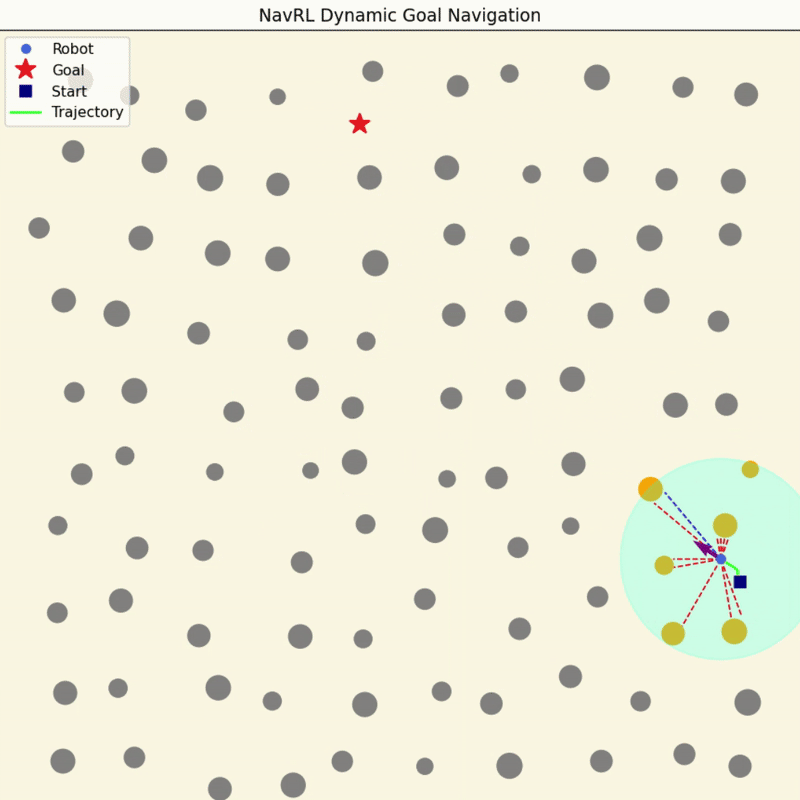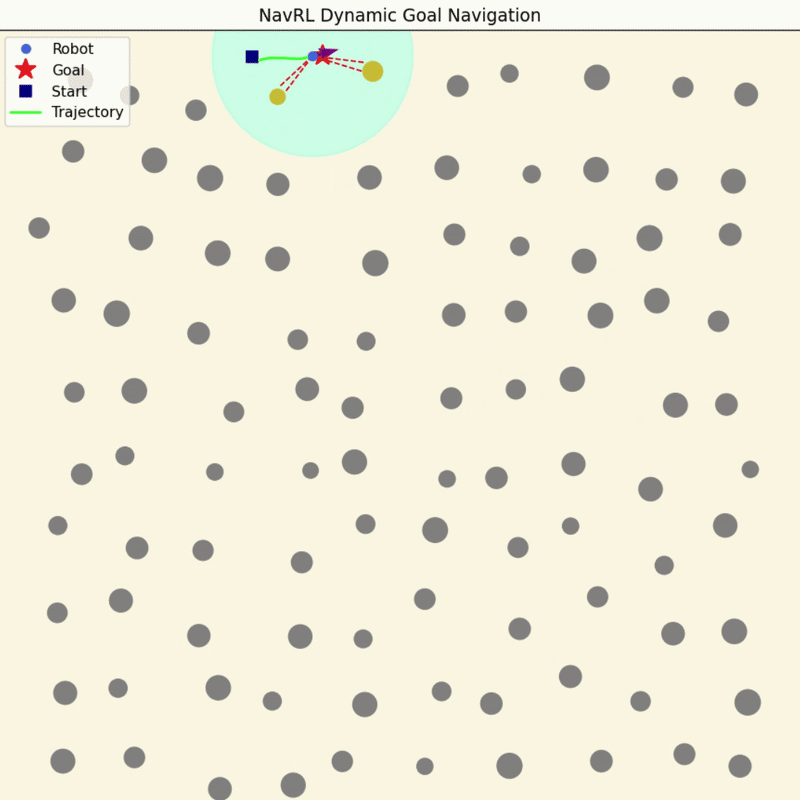 |
 |
To get started, please follow the steps in Deployment Virtual Environment to set up the Conda environment. Once the setup is complete, you can run the following three demos with the following commands:
conda activate NavRL
cd NavRL/quick-demos
# DEMO I: Navigating to a predefined goal point
python simple-navigation.py
# DEMO II: Navigating to dynamically/randomly assigned goal points
python random-navigation.py
# DEMO III: Multi-robot navigation
python multi-robot-navigation.py
I. Training in NVIDIA Isaac Sim
This section provides the steps for training your own RL agent with the NavRL framework in Isaac Sim. If you are not interested in training the agent yourself, feel free to skip this section and jump straight to the deployment section.
Isaac Sim Installation
This project was developed using Isaac Sim version 2023.1.0-hotfix.1, released in November 2023. Please make sure you download and use this exact version, as using a different version may lead to errors due to version incompatibility. Also, ensure that you have conda installed.
If you have already downloaded Isaac Sim version 2023.1.0-hotfix.1, you can skip the following steps. Otherwise, please follow the instructions below to download the legacy version of Isaac Sim, as the official installation does not support legacy version downloads.
To download Isaac Sim version 2023.1.0-hotfix.1:
a. First, follow the steps on this link to complete the Docker Container Setup.
b. Then, download the Isaac Sim to your docker container:
docker pull nvcr.io/nvidia/isaac-sim:2023.1.0-hotfix.1
docker run --name isaac-sim --entrypoint bash -it --runtime=nvidia --gpus all -e "ACCEPT_EULA=Y" --rm --network=host \
-e "PRIVACY_CONSENT=Y" \
-v ~/docker/isaac-sim/cache/kit:/isaac-sim/kit/cache:rw \
-v ~/docker/isaac-sim/cache/ov:/root/.cache/ov:rw \
-v ~/docker/isaac-sim/cache/pip:/root/.cache/pip:rw \
-v ~/docker/isaac-sim/cache/glcache:/root/.cache/nvidia/GLCache:rw \
-v ~/docker/isaac-sim/cache/computecache:/root/.nv/ComputeCache:rw \
-v ~/docker/isaac-sim/logs:/root/.nvidia-omniverse/logs:rw \
-v ~/docker/isaac-sim/data:/root/.local/share/ov/data:rw \
-v ~/docker/isaac-sim/documents:/root/Documents:rw \
nvcr.io/nvidia/isaac-sim:2023.1.0-hotfix.1
c. Move the downloaded Isaac Sim from the docker container to your local machine:
bash docker ps # check your container ID in another terminal
# Replace <id_container> with the output from the previous command
docker cp <id_container>:isaac-sim/. /path/to/local/folder # absolute path
Isaac Sim version 2023.1.0-hotfix.1 is now installed on your local machine.
NavRL Training Setup
To set up the NavRL framework, clone the repository and follow these steps (this process may take several minutes):
# Set the ISAACSIM_PATH environment variable
echo 'export ISAACSIM_PATH="path/to/isaac_sim-2023.1.0-hotfix.1"' >> ~/.bashrc
cd NavRL/isaac-training
bash setup.sh
After the setup completes, you should have created a virtual environment named
```.
### Verify Installation and Run a Training Example
Use the default parameter to run a training example with 2 robots to verify installation.
Activate NavRL virtual environment
conda activate NavRL
Run a training example with default settings
python training/scripts/train.py
If the repo is installed correctly, you should be able to see the Isaac Sim window as shown below:

### Train your own RL agent
The training environment settings and hyerparameters can be found in
```NavRL/isaac-training/training/cfg
```.
The following example demonstrates training with 1024 robots, 350 static obstacles, and 80 dynamic obstacles (an RTX 4090 is required). We recommend using [Wandb](https://wandb.ai/site/) to monitor your training and evaluation statistics.
python training/scripts/train.py headless=True env.num_envs=1024 env.num_obstacles=350
env_dyn.num_obstacles=80 wandb.mode=online
After training for a sufficient amount of time, you should observe the robots learning to avoid collisions:
https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/2294bd94-69b3-4ce8-8e91-0118cfae9bcd
## II. Deployment Virtual Environment
This section provides the minimum conda environment setup required to deploy
```NavRL
``` (including running on a real robot). If you have already created the
```NavRL
``` conda environment during the [Isaac training step](#I-Training-in-NVIDIA-Isaac-Sim), you can skip this section. To create the conda environment, run the following commands:
cd NavRL/isaac-training bash setup_deployment.sh
Once the setup is complete, a conda environment named
```NavRL
``` should be created. You can verify the installation by activating the environment:
conda activate NavRL
## III. NavRL ROS1 Deployment
This section demonstrates an example of deploying NavRL with ROS1 and Gazebo using a quadcopter robot. Ensure that your system meets the following requirements:
- Ubuntu 20.04 LTS
- ROS1 Noetic
First, install dependencies and copy the
```ros1
``` folder from this repository into your catkin workspace.
sudo apt-get install ros-noetic-mavros*
cp -r ros1 /path/to/catkin_ws/src catkin_make
Then, set the environment vairable for Gazebo models.
echo ‘source /path/to/ros1/uav_simulator/gazeboSetup.bash’ » ~/.bashrc
Note that the environment variable should be set within the catkin_ws. For example, the correct
```~./.bashrc
``` script should be
```source ~/catkin_ws/src/ros1/uav_simulator/gazeboSetup.bash
``` instead of
```source path/to/NavRL/ros1/uav_simulator/gazeboSetup.bash
```).
Finally, start the simulation and deploy NavRL navigation.
Launch the gazebo simulator
roslaunch uav_simulator start.launch
Start the perception and safety module
roslaunch navigation_runner safety_and_perception_sim.launch
Run the navigation node
conda activate NavRL rosrun navigation_runner navigation_node.py
A Gazebo window will display the environment while an RViz window presents the data. Use RViz's
```2D Nav Goal
``` tool to set the navigation target, as shown in the video below (note: the default environment and settings might be different from the video):
https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/b7cc7e2e-c01d-4e44-87e3-97271a3aaa0f
To change the environment settings, review the launch file at
```ros1/uav_simulator/launch/start.launch
```. The parameters for each module are located in
```ros1/navigation_runner/cfg/*.yaml
``` configuration files.
## IV. NavRL ROS2 Deployment
This section demonstrates an example of deploying NavRL with ROS2 and Isaac Sim using a Unitree Go2 quadruped robot. Ensure that your system meets the following requirements:
- Ubuntu 22.04 LTS
- ROS2 Humble
Before get started, please install the simulator based on [this link](https://github.com/Zhefan-Xu/isaac-go2-ros2).
First, copy the
```ros2
``` folder from this repository into your ros2 workspace.
cp -r ros2 /path/to/ros2_ws/src colcon build –symlink-install
Then, start the simulation and deploy NavRL navigation.
Launch Isaac Go2 simulator
conda activate isaaclab cd /path/to/isaac-go2-ros2 python isaac-go2-ros2.py
Start the perception and safety module
ros2 launch navigation_runner perception.launch.py ros2 launch navigation_runner safe_action.launch.py # optional
Turn on Rviz2 visualization
ros2 launch navigation_runner rviz.launch.py
Run the navigation launch
conda activate NavRL ros2 launch navigation_runner navigation.launch.py
An Isaac Sim window will display the environment while an RViz window presents the data. Use RViz's
```2D Nav Goal
``` tool to set the navigation target. The navigation example is shown in the following video:
https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/4787f503-d8a3-4d7b-9d17-7057b2cff1eb
Note that if you would like to deploy in a real robot with
```ros2 foxy
```, please switch to
```ros2-foxy
``` branch.
git checkout ros2-foxy
## V. Citation and Reference
If our work is useful to your research, please consider citing our paper.
@ARTICLE{NavRL, author={Xu, Zhefan and Han, Xinming and Shen, Haoyu and Jin, Hanyu and Shimada, Kenji}, journal={IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters}, title={NavRL: Learning Safe Flight in Dynamic Environments}, year={2025}, volume={10}, number={4}, pages={3668-3675}, keywords={Navigation;Robots;Collision avoidance;Training;Safety;Vehicle dynamics;Heuristic algorithms;Detectors;Autonomous aerial vehicles;Learning systems;Aerial systems: Perception and autonomy;reinforcement learning;collision avoidance}, doi={10.1109/LRA.2025.3546069}}
```
VI. Acknowledgement
The authors would like to express their sincere gratitude to Professor Kenji Shimada for his great support and all CERLAB UAV team members who contribute to the development of this research.
The Isaac Sim training component of the NavRL framework is built upon OmniDrones.
CONTRIBUTING

|
navrl repositoryreinforcement-learning robotics collision-avoidance robot-navigation nvidia-isaac embodied-ai isaac-sim ros1-noetic ros2-humble |
|
|

|
navrl repositoryreinforcement-learning robotics collision-avoidance robot-navigation nvidia-isaac embodied-ai isaac-sim ros1-noetic ros2-humble |
|
|

|
navrl repositoryreinforcement-learning robotics collision-avoidance robot-navigation nvidia-isaac embodied-ai isaac-sim ros1-noetic ros2-humble |
|
|

|
navrl repositoryreinforcement-learning robotics collision-avoidance robot-navigation nvidia-isaac embodied-ai isaac-sim ros1-noetic ros2-humble |
|
|




