Repository Summary
| Description | Precisely stamped URG ROS driver node. |
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/seqsense/urg_stamped.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2024-12-16 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| CI status | No Continuous Integration |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (0)
Good First Issues (0) Pull Requests to Review (0) |
Packages
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| urg_stamped | 0.4.0 |
README
urg_stamped
Precisely and accurately stamped URG driver for ROS
Background and Algorithm
2D-LIDAR URG series provides 1ms resolution timestamp and exclusive clock synchronization mode. It was hard to compensate clock drift during measurement using them. Also, the resolution of the timestamp was not enough for a high-speed motion of the sensor.
So, urg_stamped estimates sub-millisecond by the following algorithm:
- Select the algorithms based on the sensor model
- UTM: UTM-30LX-EW
- UST(UUST1): UST-*LX, UST-*LC with firmware version <4.0.0
- UST(UUST2-Unfixed): UST-*LX, UST-*LC with firmware version >=4.0.0 and <4.0.3
- UST(UUST2-Fixed): UST-*LX, UST-*LC with firmware version >=4.0.3
- Determine sensor internal clock state (clock offset and gain) using TM command (Triggered by 30s timer by default)
- UTM/UST(UUST1)/UST(UUST2-Fixed): (These models respond to TM command as expected in SCIP2 protocol)
-
- Observe sub-millisecond clock offset by finding increment of millisecond resolution sensor timestamp
-
- Observe clock gain from multiple observations of the clock offset
-
- UST(UUST2-Unfixed): (This model responds to TM command on the next 5ms frame which breaks SCIP2’s time synchronization logic)
-
- Request TM command many times with different timing
-
- Filter responses with large delay
-
- Collect sensor response timings which should be synchronized to the sensor timestamp increment
-
- Observe sub-millisecond clock offset based on the sensor response timings and sensor timestamps
-
- Observe clock gain from multiple observations of the clock offset
-
- UTM/UST(UUST1)/UST(UUST2-Fixed): (These models respond to TM command as expected in SCIP2 protocol)
- Determine scan origin time and interval
- UTM: (UTM sends scan data right after the scan is finished)
-
- Observe scan timing based on scan data arrival time
-
- UST: (UST sends scan data on the next 1ms frame after the scan is finished)
-
- Find sensor scan timestamp jitter
-
- Observe scan origin time and scan interval using scan timestamp jitter
-
- UTM: (UTM sends scan data right after the scan is finished)
- Calculate sub-millisecond scan timestamp based on the observed scan origin time and scan interval
LaserScan data is stopped during sensor internal clock estimation which takes at most ~100ms on UTM/UST(UUST1)/UST(UUST2-Fixed) and ~1s on UST(UUST2-Unfixed). To avoid stopping all sensors at once on multi-sensor configuration, urg_stamped automatically adjusts the timing of sensor internal clock estimation based on the messages on urg_stamped_sync_start topic.
Usages
Topics and major parameters are designed to be compatible with urg_node.
Published Topics
-
scan (
sensor_msgs::LaserScan)
Parameters
urg_node compatible parameters
- ip_address (string): device IP address
- ip_port (int): device TCP/IP port
- frame_id (string): frame_id of published scans
- publish_intensity (bool): fill intensity field if true
- error_limit (int): reset the sensor and exit if errors occur more than this count
urg_stamped specific parameters
- clock_estim_interval (double): sensor internal clock state estimation interval in seconds (dropping several scans during estimation)
- fallback_on_continuous_scan_drop (int): fallback to naive 1ms accuracy timestamp if failed to estimate sub-millisecond timestamp more than this value
Known Limitations
- Timestamp estimation is designed for sensors connected by ethernet interface.
- Tested on the following sensor models:
- UTM-30LX-EW
- UST-05LX
- UST-20LX
- UST-30LC
- UUST2 model of UST series (firmware version >=4.0.0) takes longer time to perform the time synchronization due to the sensor’s behavior.
- Tested on the following sensor models:
- Some scans are dropped due to the clock synchronization and delay estimation.
Comparison with urg_node
Configurations
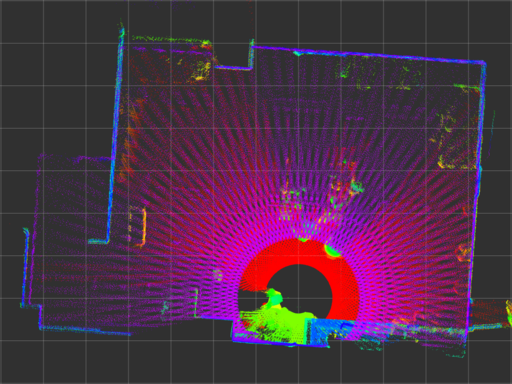
Three UTM-30LX-EWs are mounted on a velocity controlled turntable, as shown below, to reconstruct 3-D point cloud from 2-D scans. The accuracy of the timestamp affects offset and precision of the timestamp affects the distribution of the pointcloud.

Results
[!NOTE]
Following results are based on the previous algorithm (urg_stamped<0.2.0). They will be updated later.
The image below shows point cloud with 1 rad/s of the turntable which can be assumed as a reference. (decay time of the point cloud: 10 seconds)
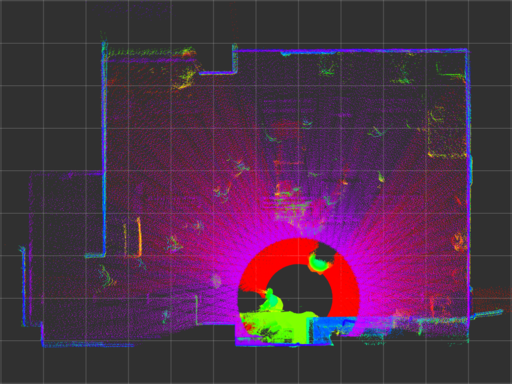
urg_node has large error even if calibrate_time and synchronize_time options are enabled (captioned as urg_node (sync)).
urg_stamped has better timestamp characteristics comparing with urg_node.
| 10 rad/s | 20 rad/s | |
|---|---|---|
| urg_stamped | 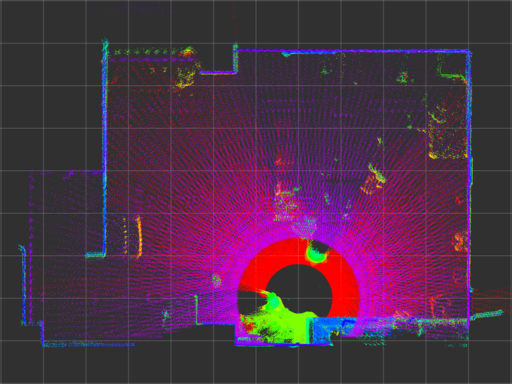 |
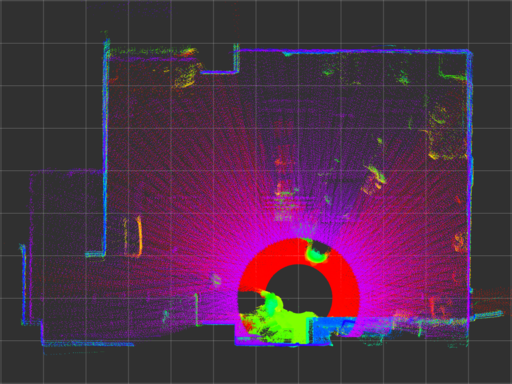 |
| urg_node | 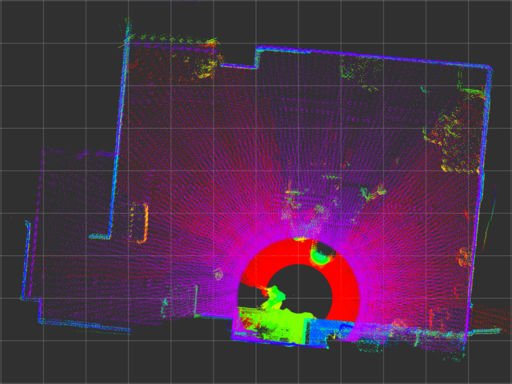 |
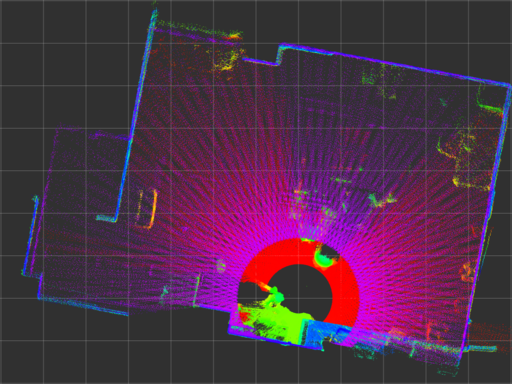 |
| urg_node (sync) |
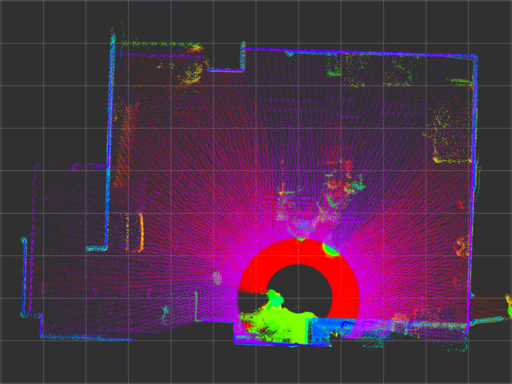 |
 |
CONTRIBUTING
Repository Summary
| Description | Precisely stamped URG ROS driver node. |
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/seqsense/urg_stamped.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | master |
| Last Updated | 2024-12-16 |
| Dev Status | DEVELOPED |
| CI status | No Continuous Integration |
| Released | RELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (0)
Good First Issues (0) Pull Requests to Review (0) |
Packages
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| urg_stamped | 0.4.0 |
README
urg_stamped
Precisely and accurately stamped URG driver for ROS
Background and Algorithm
2D-LIDAR URG series provides 1ms resolution timestamp and exclusive clock synchronization mode. It was hard to compensate clock drift during measurement using them. Also, the resolution of the timestamp was not enough for a high-speed motion of the sensor.
So, urg_stamped estimates sub-millisecond by the following algorithm:
- Select the algorithms based on the sensor model
- UTM: UTM-30LX-EW
- UST(UUST1): UST-*LX, UST-*LC with firmware version <4.0.0
- UST(UUST2-Unfixed): UST-*LX, UST-*LC with firmware version >=4.0.0 and <4.0.3
- UST(UUST2-Fixed): UST-*LX, UST-*LC with firmware version >=4.0.3
- Determine sensor internal clock state (clock offset and gain) using TM command (Triggered by 30s timer by default)
- UTM/UST(UUST1)/UST(UUST2-Fixed): (These models respond to TM command as expected in SCIP2 protocol)
-
- Observe sub-millisecond clock offset by finding increment of millisecond resolution sensor timestamp
-
- Observe clock gain from multiple observations of the clock offset
-
- UST(UUST2-Unfixed): (This model responds to TM command on the next 5ms frame which breaks SCIP2’s time synchronization logic)
-
- Request TM command many times with different timing
-
- Filter responses with large delay
-
- Collect sensor response timings which should be synchronized to the sensor timestamp increment
-
- Observe sub-millisecond clock offset based on the sensor response timings and sensor timestamps
-
- Observe clock gain from multiple observations of the clock offset
-
- UTM/UST(UUST1)/UST(UUST2-Fixed): (These models respond to TM command as expected in SCIP2 protocol)
- Determine scan origin time and interval
- UTM: (UTM sends scan data right after the scan is finished)
-
- Observe scan timing based on scan data arrival time
-
- UST: (UST sends scan data on the next 1ms frame after the scan is finished)
-
- Find sensor scan timestamp jitter
-
- Observe scan origin time and scan interval using scan timestamp jitter
-
- UTM: (UTM sends scan data right after the scan is finished)
- Calculate sub-millisecond scan timestamp based on the observed scan origin time and scan interval
LaserScan data is stopped during sensor internal clock estimation which takes at most ~100ms on UTM/UST(UUST1)/UST(UUST2-Fixed) and ~1s on UST(UUST2-Unfixed). To avoid stopping all sensors at once on multi-sensor configuration, urg_stamped automatically adjusts the timing of sensor internal clock estimation based on the messages on urg_stamped_sync_start topic.
Usages
Topics and major parameters are designed to be compatible with urg_node.
Published Topics
-
scan (
sensor_msgs::LaserScan)
Parameters
urg_node compatible parameters
- ip_address (string): device IP address
- ip_port (int): device TCP/IP port
- frame_id (string): frame_id of published scans
- publish_intensity (bool): fill intensity field if true
- error_limit (int): reset the sensor and exit if errors occur more than this count
urg_stamped specific parameters
- clock_estim_interval (double): sensor internal clock state estimation interval in seconds (dropping several scans during estimation)
- fallback_on_continuous_scan_drop (int): fallback to naive 1ms accuracy timestamp if failed to estimate sub-millisecond timestamp more than this value
Known Limitations
- Timestamp estimation is designed for sensors connected by ethernet interface.
- Tested on the following sensor models:
- UTM-30LX-EW
- UST-05LX
- UST-20LX
- UST-30LC
- UUST2 model of UST series (firmware version >=4.0.0) takes longer time to perform the time synchronization due to the sensor’s behavior.
- Tested on the following sensor models:
- Some scans are dropped due to the clock synchronization and delay estimation.
Comparison with urg_node
Configurations
Three UTM-30LX-EWs are mounted on a velocity controlled turntable, as shown below, to reconstruct 3-D point cloud from 2-D scans. The accuracy of the timestamp affects offset and precision of the timestamp affects the distribution of the pointcloud.

Results
[!NOTE]
Following results are based on the previous algorithm (urg_stamped<0.2.0). They will be updated later.
The image below shows point cloud with 1 rad/s of the turntable which can be assumed as a reference. (decay time of the point cloud: 10 seconds)

urg_node has large error even if calibrate_time and synchronize_time options are enabled (captioned as urg_node (sync)).
urg_stamped has better timestamp characteristics comparing with urg_node.
| 10 rad/s | 20 rad/s | |
|---|---|---|
| urg_stamped |  |
 |
| urg_node |  |
 |
| urg_node (sync) |
 |
 |
