Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 0.0.0 |
| License | TODO: License declaration |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Description | ROS2 was developed for the Realman robot (http://www.realman-robotics.com/). |
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/realmanrobot/ros2_rm_robot.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | humble |
| Last Updated | 2025-01-09 |
| Dev Status | UNMAINTAINED |
| CI status | No Continuous Integration |
| Released | UNRELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (0)
Good First Issues (0) Pull Requests to Review (0) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- rm
Authors
Content
- 1.rm_example Package Description
- 2.rm_example Package Use
- 2.1Changing the work coordinate system
- 2.2Get the current state message of the robotic arm
- 2.3MoveJ motion of the robotic arm
- 2.4MoveJ_P motion of the robotic arm
- 2.5MoveL motion of the robotic arm
- 3.rm_example Package Architecture Description
- 3.1Overview of Package Files
- 4.rm_example Topic Description
- 4.1rm_change_work_frame topic description
- 4.2rm_get_state topic description
- 4.3movej_demo topic description
- 4.4movejp_demo topic description
- 4.5movel_demo topic description
rm_example_Package_Description
rm_bringup package is used for realizing some basic robotic arm functions. And we can also refer to the code to realize other robotic arm functions. This package is introduced in detail in the following aspects.
- 1.Package use.
- 2.Package architecture description.
- 3.Package topic description.
Through the introduction of the three parts, it can help you: - 1.Understand the package use.
- 2.Familiar with the file structure and function of the package.
- 3.Familiar with the topic related to the package for easy development and use.
Source code address:https://github.com/RealManRobot/ros2_rm_robot.git.
rm_example_Package_Use
Changing_the_work_coordinate_system
First, we need to run the underlying driver node of the robotic arm rm_driver.
rm@rm-desktop:~$ ros2 launch rm_driver rm_<arm_type>_driver.launch.py
In practice, the above
rm@rm-desktop:~$ ros2 launch rm_driver rm_65_driver.launch.py
After successfully launching the node, execute the following commands to replace the node in the work coordinate system.
rm@rm-desktop:~$ ros2 run rm_example rm_change_work_frame
The following command pops up to indicate successful replacement.
 Enter the following commands in the end for verification, first subscribe to the current work coordinate system topic.
Enter the following commands in the end for verification, first subscribe to the current work coordinate system topic.
rm@rm-desktop:~$ ros2 topic echo /rm_driver/get_curr_workFrame_result
Then publish the request of the current coordinate system.
rm@rm-desktop:~$ ros2 topic pub --once /rm_driver/get_curr_workFrame_cmd std_msgs/msg/Empty "{}"
You can see the following interface pop up at the end.

Get_the_current_state_message_of_the_robotic_arm
First, we need to run the underlying driver node of the robotic arm rm_driver.
rm@rm-desktop:~$ ros2 launch rm_driver rm_<arm_type>_driver.launch.py
In practice, the above
rm@rm-desktop:~$ ros2 launch rm_driver rm_65_driver.launch.py
After successfully launching the node, execute the following commands to obtain the current state of the robotic arm node.
rm@rm-desktop:~$ ros2 run rm_example rm_get_state
The following command pops up to indicate successful replacement.
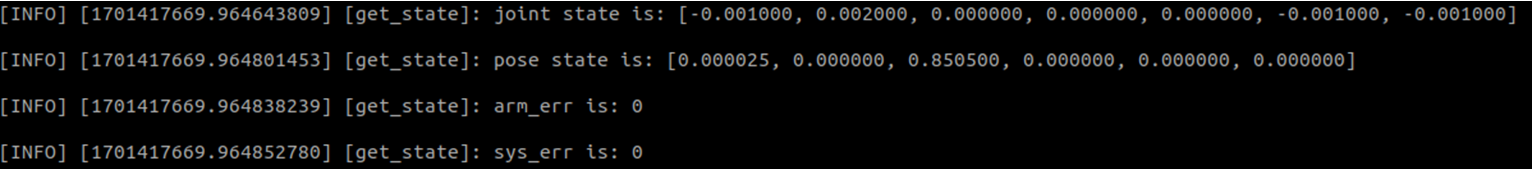 What is displayed in the interface is the current angle message of the robotic arm, as well as the current end coordinate position and Euler angle posture message of the robotic arm.
What is displayed in the interface is the current angle message of the robotic arm, as well as the current end coordinate position and Euler angle posture message of the robotic arm.
MoveJ_motion_of_the_robotic_arm
Through the following commands, we can control the joint MoveJ motion of the robotic arm. First, we need to run the underlying driver node of the robotic arm rm_driver.
rm@rm-desktop:~$ ros2 launch rm_driver rm_<arm_type>_driver.launch.py
In practice, the above
rm@rm-desktop:~$ ros2 launch rm_driver rm_65_driver.launch.py
After successfully launching the node, execute the following commands to control the movement of the robotic arm.
rm@rm-desktop:~$ ros2 launch rm_example rm_<dof>_movej.launch.py
dof represents the current degree of freedom message of the arm, and the parameters can be selected as 6dof and 7dof.
For example, when starting the 7-axis robotic arm, the following commands are needed.
rm@rm-desktop:~$ ros2 launch rm_example rm_7dof_movej.launch.py
After successful running, the joint of the robotic arm rotates and the interface displays as follows.
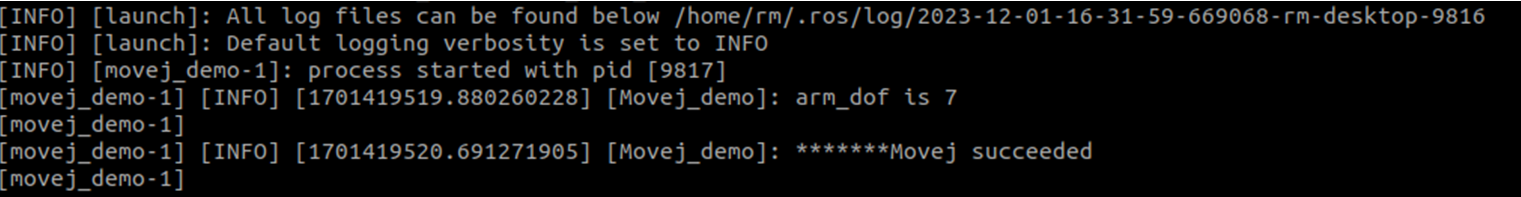
MoveJ_P_motion_of_the_robotic_arm
Through the following commands, we can control the joint MoveJ_P motion of the robotic arm.
First, we need to run the underlying driver node of the robotic arm rm_driver.
rm@rm-desktop:~$ ros2 launch rm_driver rm_<arm_type>_driver.launch.py
In practice, the above
rm@rm-desktop:~$ ros2 launch rm_driver rm_65_driver.launch.py
After successfully launching the node, execute the following commands to control the movement of the robotic arm.
rm@rm-desktop:~$ ros2 run rm_example movejp_demo
Arm version is GEN72, execute the following commands to control the movement of the robotic arm.
rm@rm-desktop:~$ ros2 run rm_example movejp_gen72_demo
After successful execution, the interface appears as follows, and the robotic arm will move to the specified pose.

MoveL_motion_of_the_robotic_arm
Through the following commands, we can control the joint MoveL motion of the robotic arm.
First, we need to run the underlying driver node of the robotic arm rm_driver.
rm@rm-desktop:~$ ros2 launch rm_driver rm_<arm_type>_driver.launch.py
In practice, the above
rm@rm-desktop:~$ ros2 launch rm_driver rm_65_driver.launch.py
After successfully launching the node, execute the following commands to control the movement of the robotic arm.
rm@rm-desktop:~$ ros2 run rm_example movel_demo
Arm version is GEN72, execute the following commands to control the movement of the robotic arm.
rm@rm-desktop:~$ ros2 run rm_example movel_gen72_demo
After successful execution, the interface appears as follows, and the robotic arm performs two motions. Firstly, it moves to the specified pose through MoveJP, and then performs joint motion through MoveL.

rm_example_Package_Architecture_Description
Overview_of_Package_Files
The current rm_driver package is composed of the following files.
├── CMakeLists.txt # compilation rule file
├── doc
│ ├── rm_example10.png
│ ├── rm_example11.png
│ ├── rm_example1.png
│ ├── rm_example2.png
│ ├── rm_example3.png
│ ├── rm_example4.png
│ ├── rm_example5.png
│ ├── rm_example6.png
│ ├── rm_example7.png
│ ├── rm_example8.png
│ └── rm_example9.png
├── include
│ └── rm_example
├── launch
│ ├── rm_6dof_movej.launch.py # 6 degrees of freedom MoveJ movement launch file
│ └── rm_7dof_movej.launch.py # 7 degrees of freedom MoveJ movement launch file
├── package.xml
└── src
├── api_ChangeWorkFrame_demo.cpp # source file to change the work coordinate system
├── api_Get_Arm_State_demo.cpp # source file to get the robotic arm's state
├── api_MoveJ_demo.cpp # MoveJ motion source file
├── api_MoveJP_demo.cpp # MoveJP motion source file
├── api_MoveJP_Gen72_demo.cpp # GEN72 MoveJP motion source file
├── api_MoveL_demo.cpp # MoveL motion source file
└── api_MoveL_Gen72_demo.cpp # GEN72 MoveL motion source file
rm_example_Topic_Description
rm_change_work_frame_topic_description
The following is the data communication diagram of this node:
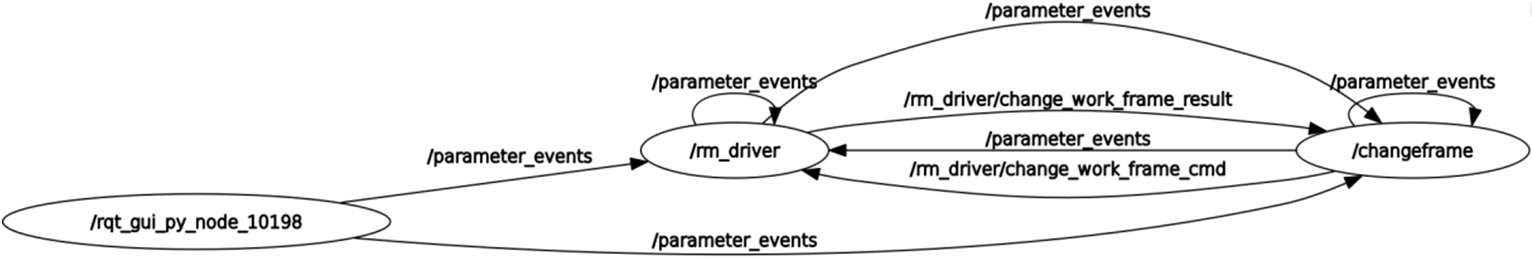 You can see that the main communication topics between /changeframe node and /rm_driver are /rm_driver/change_work_frame_result and /rm_driver/change_work_frame_cmd. / rm_driver/change_work_frame_cmd is the release of the switch request and the switch target coordinates, and /rm_driver/change_work_frame_result is the switch result.
You can see that the main communication topics between /changeframe node and /rm_driver are /rm_driver/change_work_frame_result and /rm_driver/change_work_frame_cmd. / rm_driver/change_work_frame_cmd is the release of the switch request and the switch target coordinates, and /rm_driver/change_work_frame_result is the switch result.
rm_get_state_topic_description
The following is the data communication diagram of this node:
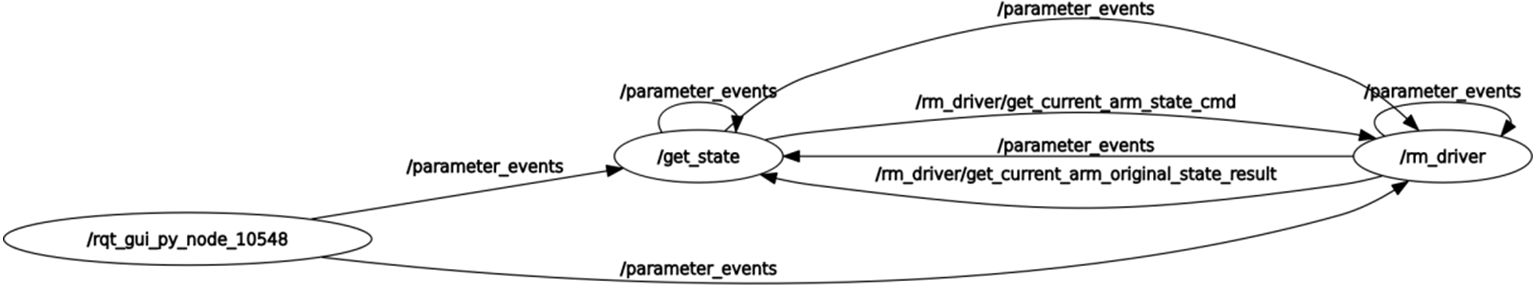 You can see that the main communication topics between the /get_state node and /rm_driver are /rm_driver/get_current_arm_state_cmd and /rm_driver/get_current_arm_original_state_result. / rm_driver/get_current_arm_state_cmd is the request to get the current state of the arm, and /rm_driver/get_current_arm_original_state_result is the switch result.
You can see that the main communication topics between the /get_state node and /rm_driver are /rm_driver/get_current_arm_state_cmd and /rm_driver/get_current_arm_original_state_result. / rm_driver/get_current_arm_state_cmd is the request to get the current state of the arm, and /rm_driver/get_current_arm_original_state_result is the switch result.
movej_demo_topic_description
The following is the data communication diagram of this node:
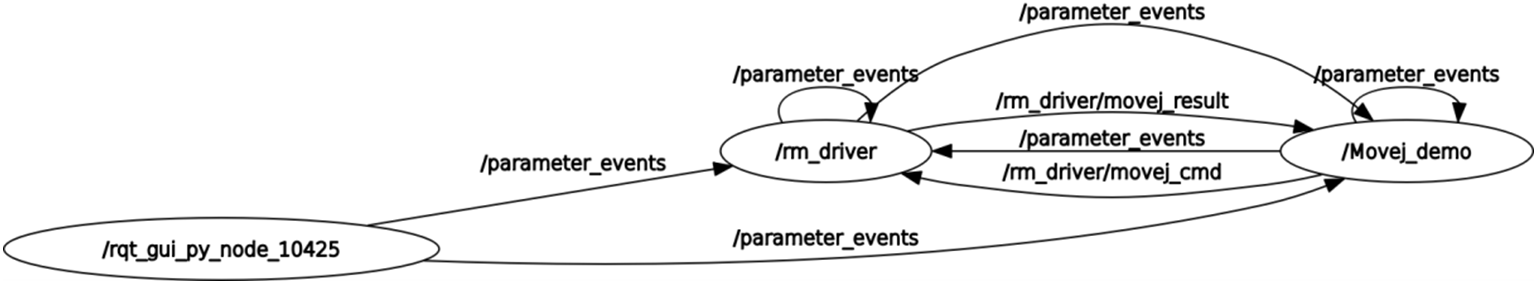 You can see that the main communication topics between the /Movej_demo node and /rm_driver are /rm_driver/movej_cmd and /rm_driver/movej_result. / rm_driver/movej_cmd is the request to control the motion of the robotic arm, which will release the radian information of each joint that needs to be moved, and /rm_driver/movej_result is the motion result.
You can see that the main communication topics between the /Movej_demo node and /rm_driver are /rm_driver/movej_cmd and /rm_driver/movej_result. / rm_driver/movej_cmd is the request to control the motion of the robotic arm, which will release the radian information of each joint that needs to be moved, and /rm_driver/movej_result is the motion result.
movejp_demo_topic_description
The following is the data communication diagram of this node:
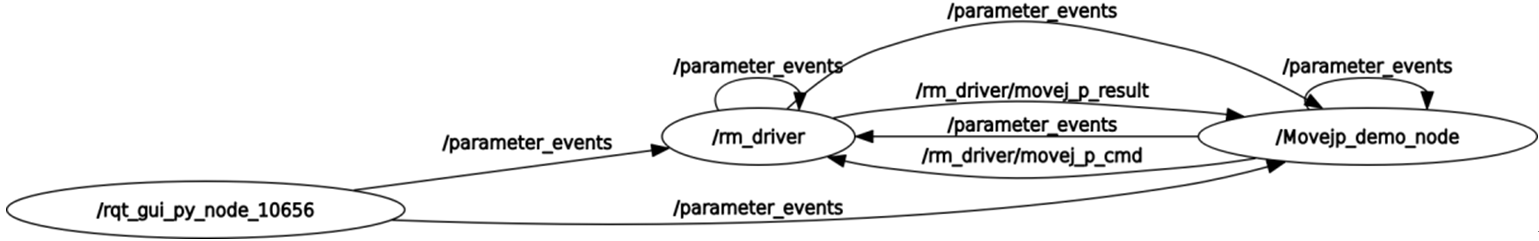 You can see that the main communication topics between the /Movejp_demo_node node and /rm_driver are /rm_driver/movej_p_cmd and rm_driver/movej_p_result. / rm_driver/movej_p_cmd is the request to control the motion planning of the robotic arm, which will publish the coordinates of the target point to be moved, and /rm_driver/movej_p_result is the motion result.
You can see that the main communication topics between the /Movejp_demo_node node and /rm_driver are /rm_driver/movej_p_cmd and rm_driver/movej_p_result. / rm_driver/movej_p_cmd is the request to control the motion planning of the robotic arm, which will publish the coordinates of the target point to be moved, and /rm_driver/movej_p_result is the motion result.
movel_demo_topic_description
The following is the data communication diagram of this node:
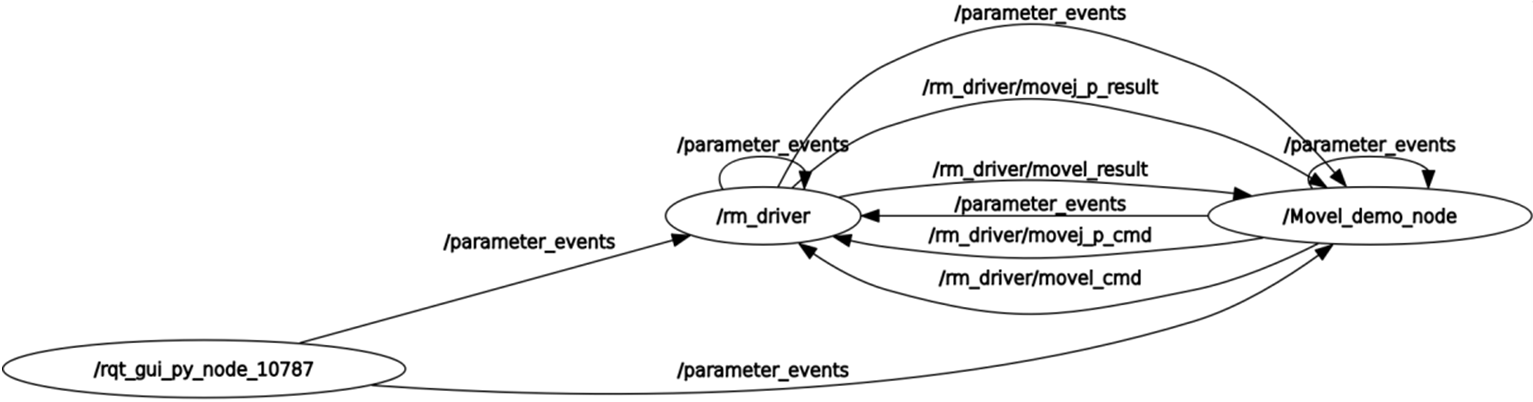 You can see that the main communication topics between the /Movel_demo_node node and /rm_driver are /rm_driver/movej_p_cmd and /rm_driver/movej_p_result, and /rm_driver/movel_cmd and /rm_driver/movel_result. / rm_driver/movej_p_cmd is the request to control the motion planning of the robotic arm, which will publish the coordinates of the target point to be moved first, /rm_driver/movej_p_result is the motion result. After reaching the first point, we reach the second point through linear motion, we can publish the pose of the second point through /rm_driver/movel_cmd, and the topic of /rm_driver/movel_result is the result of the motion.
You can see that the main communication topics between the /Movel_demo_node node and /rm_driver are /rm_driver/movej_p_cmd and /rm_driver/movej_p_result, and /rm_driver/movel_cmd and /rm_driver/movel_result. / rm_driver/movej_p_cmd is the request to control the motion planning of the robotic arm, which will publish the coordinates of the target point to be moved first, /rm_driver/movej_p_result is the motion result. After reaching the first point, we reach the second point through linear motion, we can publish the pose of the second point through /rm_driver/movel_cmd, and the topic of /rm_driver/movel_result is the result of the motion.
