Package Summary
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Version | 0.1.1 |
| License | Apache License 2.0 |
| Build type | AMENT_CMAKE |
| Use | RECOMMENDED |
Repository Summary
| Description | A framework for orchestration |
| Checkout URI | https://github.com/osrf/nexus.git |
| VCS Type | git |
| VCS Version | main |
| Last Updated | 2025-04-30 |
| Dev Status | UNMAINTAINED |
| CI status | No Continuous Integration |
| Released | UNRELEASED |
| Tags | No category tags. |
| Contributing |
Help Wanted (0)
Good First Issues (0) Pull Requests to Review (0) |
Package Description
Additional Links
Maintainers
- John Tan
Authors
nexus_motion_planner
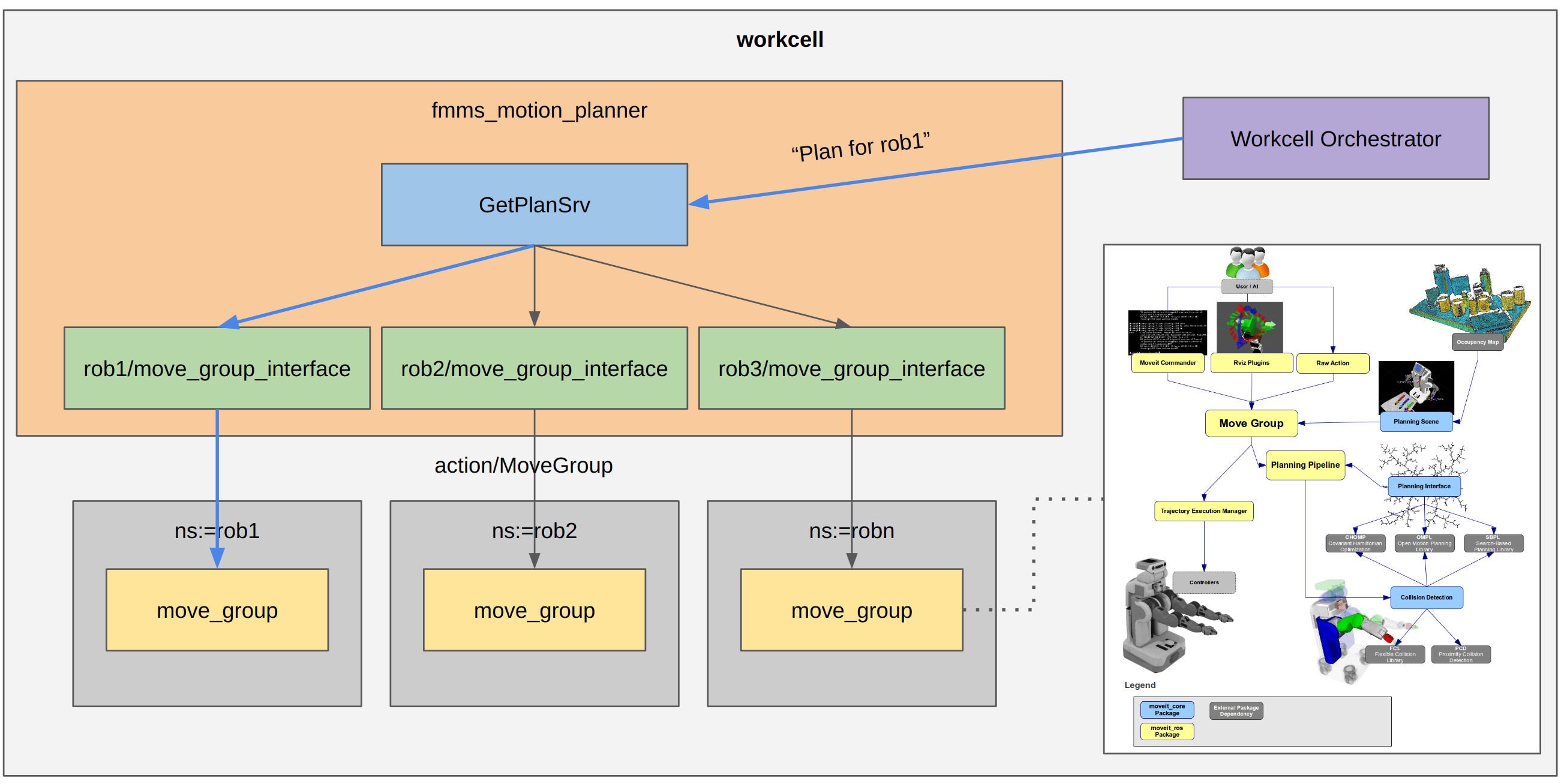
This package implements the Motion Planner Server as a lifecycle node managed by the workcell orchestrator.
The Motion Planner Server implements a standardized ROS2 Interface nexus_motion_planner_msgs::GetMotionPlan to receive motion planning requests from the Workcell Orchestrator.
This motion plan in the form of a trajectory_msgs/JointTrajectory will be forwarded by the Workcell Orchestrator to the Controller Server for execution via another action, the trajectory execution works independently of Motion Planner Server.
The Motion Planner Server is meant to be:
- Hardware-agnostic
- New robots can be configured and set up easily with the help of moveit setup assistant.
- Planner-agnostic
- Plugin-based.
- Planners can be easily added via implementation of
moveit_core::planning_interface
- Database Vendor-agnostic
- Plugin-based.
- Alternative databases can be easily integrated via implementation of
warehouse_ros::DatabaseLoader - Currently available databases are
SQLite3andMongoDB
What Motion Planner Server does not do:
- Execute robot trajectories. This is done by the Controller Server which uses the JointTrajectoryController to execute trajectory_msgs/JointTrajectory plans from Motion Planner Server.
The nexus_motion_planner::motion_planner_server is currently a wrapper around MoveGroupInterface which simplifies querying and configuring move_group. The motion_planner_server can be configured to setup interfaces with multiple move_groups and thus becomes a manager of move_group_interfaces. When a motion plan request from the workcell orchestrator is received for one of the configured robots, it simply queries the move_group of that robot via its move_group_interface.
The use_move_group_interfaces parameter is set True by default which enables the above behavior.
For future work, the motion_planner_server may directly initialize PlanningPipelines for each robot thereby skipping the need to interface with move_group.
Quick start
1. Set up configuration parameters
Motion Planner Server allows you to request plans for each individual robot. These robots can be configured to have a default planning_group, their own specific planner_plugin params and kinematic_plugin solver params.
Explanation of each configuration parameter are commented in planner_params.yaml
2. Launch the motion planner server
A demo script that launches move_group along with the motion_planner_server is included.
By default the abb_irb1300 robot is used.
ros2 launch nexus_motion_planner demo_planner_server.launch.py
To try a different robot, launch with some parameter substitutions.
ros2 launch nexus_motion_planner demo_planner_server.launch.py support_package:=abb_irb910sc_support robot_xacro_file:=irb910sc_3_45.xacro moveit_config_package:=abb_irb910sc_3_45_moveit_config moveit_config_file:=abb_irb910sc_3_45.srdf.xacro
3. Configuring and activating up the Motion Planner Server lifecycle node
Configuring should start up the service servers, services and any suscribers.
Activation should start up the moveit components (i.e. Planning Pipeline, Planning Scene Monitor and Moveit Visualization Tools).
ros2 lifecycle set /motion_planner_server configure
ros2 lifecycle set /motion_planner_server activate
4. Start an example service client for sending motion planning tasks
Refer to src/test_request.cpp for an example on how to interact with the Motion Planner Server via the nexus_motion_planner_msgs::GetMotionPlan service. Below are some example poses/joint values given for manual testing.
IRB910SC
# Specifying end-effector poses. Optionally, start value can be specified "-s <pose_string>"
# Home state (frame_id: item): 0.150,-0.200,0.051,1,0,0,0
# paste_item state (frame_id: item): 0.145,-0.166,-0.053,1.00,0.0,0.0,0.0
# pick_item state (frame_id: item): -0.384,0.193,0.046,1.00,0.0,0.0,0.0
ros2 run nexus_motion_planner test_request -name abb_irb910sc -frame_id item -goal_type 0 -t -0.384,0.193,0.046,1.00,0.0,0.0,0.0
# Specifying joint values. Optionally, start value can be specified "-sj <joint_values_string>"
# home state: 0,0,0,0
# paste_item state: 0,0,-0.1,0
# pick_item state: 1.2,1.2,-0.1,0.1
ros2 run nexus_motion_planner test_request -name abb_irb910sc -frame_id item -goal_type 1 -tj 1.2,1.2,-0.1,0.1
IRB1300
# Specifying end-effector poses. Optionally, start value can be specified "-s <pose_string>"
# Home state: 0.654250,0.0,1.143500,0.0,0.707107,0.0,0.707107
# paste_item state: 0.794981,0.000000,0.063564,0.000000,0.707107,0.000000,0.707107
# pick_item state: 0.054310,0.765854,0.677203,-0.498732,0.592116,0.454073,0.441002
ros2 run nexus_motion_planner test_request -name abb_irb1300 -frame_id item -goal_type 0 -t 0.794981,0.000000,0.063564,0.000000,0.707107,0.000000,0.707107
# Specifying joint values. Optionally, start value can be specified "-sj <joint_values_string>"
# home state: 0,0,0,0,0,0
# paste_item state: 0,1.3,0,0,0,0
# pick_item state: 1.5,0.5,0.5,0,-0.8,0.1
ros2 run nexus_motion_planner test_request -name abb_irb1300 -frame_id item -goal_type 1 -tj 1.5,0.5,0.5,0,-0.8,0.1
Note: For debugging purposes, you can also add a
-send_trajflag which will publish a joint trajectory message on “/manipulator_controller/joint_trajectory”.
You can also define the frame_id of the start/goal pose with the
-frame_idflag.
Re-using cached motion plans
All paths will be saved to the database by default. First a string is obtained by appending the planning_group, start and goal values. This string is then hashed into a plan_id and saved under the plan_id into the collection that corresponds to the robot. Subsequent plans using the same planning_group, start and end point should be fetched from cache and not regenerated.
Expected interactions between workcell orchestrator and motion planner server
Services
- “/motion_planner_server/plan” nexus_motion_planner_msgs::srv::GetMotionPlan: Service for requesting motion plan.
- ”~/change_state” lifecycle_msgs::srv::ChangeState: Set lifecycle states
- ”~/get_state” lifecycle_msgs::srv::GetState: Get lifecycle states
Topics
- ”~/motion_plan_request” moveit_msgs::msg::MotionPlanRequest: Publish Motion Plan Request taken by Motion Planner Server, used for debugging purposes.
Database Schema
Right now, the database plugin used is warehouse_ros_sqlite, this is because mongoDB is not supported on Jammy yet (as of 25/08/2022).
To avoid writing/reading to specific SQLite files, the warehouse_host is set to “:memory:” (i.e. In-memory).
This means that all cached motion plans will be lost upon restart of the node. During deployment, it should write to storage to survive restarts.
In the future, the move will be made to use warehouse_ros_mongo the non-relational database structure would be more intuitive for storing/organising motion plans.
Useful links:
Issues
-
If you are experiencing SEGFAULT, make sure to have installed all the ROS Dependencies from the package.xml via
rosdep - Database
- Currently no way of handling if motion plan database gets too large.
- Fetching of cached paths:
- No collision checks are done when cached paths are used. This is done with the assumption that the planning scene is fixed.
Changelog for package nexus_motion_planner
0.1.1 (2023-11-20)
- Use parent node options (#24)
- Contributors: Yadunund
0.1.0 (2023-11-06)
- Provides
nexus_motion_plannernode which can be queried for motion plans for manipulators.
Wiki Tutorials
Package Dependencies
| Deps | Name |
|---|---|
| ament_cmake | |
| moveit_ros | |
| warehouse_ros_sqlite | |
| xacro | |
| abb_irb910sc_3_45_moveit_config | |
| abb_irb910sc_support | |
| abb_irb1300_10_115_moveit_config | |
| abb_irb1300_support | |
| ament_cmake_pytest | |
| ament_cmake_uncrustify | |
| launch_pytest | |
| launch_testing_ament_cmake | |
| rmw_cyclonedds_cpp | |
| moveit_configs_utils | |
| moveit_resources | |
| rmf_utils | |
| robot_state_publisher | |
| ros2_control | |
| backward_ros | |
| nexus_endpoints | |
| geometry_msgs | |
| moveit_ros_planning_interface | |
| rclcpp | |
| rclcpp_action | |
| rclcpp_lifecycle | |
| tf2_ros | |
| trajectory_msgs |
System Dependencies
Dependant Packages
| Name | Deps |
|---|---|
| nexus_demos |
